“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been suggested as a potential antihypertensive drug.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been suggested as a potential antihypertensive drug.
The aim of our study was to investigate its vasodilatory effect in isolated human pulmonary arteries (hPAs) and rat small mesenteric arteries (sMAs).
METHODS:
Vascular effects of CBD were examined in hPAs obtained from patients during resection of lung carcinoma and sMAs isolated from spontaneously hypertensive (SHR); 11-deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA-salt) hypertensive rats or their appropriate normotensive controls using organ bath and wire myography, respectively.
RESULTS:
CBD induced almost full concentration-dependent vasorelaxation in hPAs and rat sMAs. In hPAs, it was insensitive to antagonists of CB1 (AM251) and CB2 (AM630) receptors but it was reduced by endothelium denudation, cyclooxygenase inhibitors (indomethacin and nimesulide), antagonists of prostanoid EP4 (L161982), IP (Cay10441), vanilloid TRPV1 (capsazepine) receptors and was less potent under KCl-induced tone and calcium-activated potassium channel (KCa) inhibitors (iberiotoxin, UCL1684 and TRAM-34) and in hypertensive, overweight and hypercholesteremic patients. The time-dependent effect of CBD was sensitive to the PPARγ receptor antagonist GW9662. In rats, the CBD potency was enhanced in DOCA-salt and attenuated in SHR. The CBD-induced relaxation was inhibited in SHR and DOCA-salt by AM251 and only in DOCA-salt by AM630 and endothelium denudation.
CONCLUSION:
The CBD-induced relaxation in hPAs that was reduced in hypertensive, obese and hypercholesteremic patients was endothelium-dependent and mediated via KCa and IP, EP4, TRPV1 receptors. The CBD effect in rats was CB1-sensitive and dependent on the hypertension model. Thus, modification of CBD-mediated responses in disease should be considered when CBD is used for therapeutic purposes.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31800399
https://insights.ovid.com/crossref?an=00004872-900000000-97067

 “There is considerable interest in the use of cannabinoids for symptom control in palliative care, but there is little high-quality evidence to guide clinical practice.
“There is considerable interest in the use of cannabinoids for symptom control in palliative care, but there is little high-quality evidence to guide clinical practice. “A 64 year old male heating engineer was investigated for a persistent cough and found to have epithelioid mesothelioma with pleural effusion, lung nodules and increased thoracic lymph nodes. He declined standard of care treatment following his own research and he was enrolled in a named patient programme of IMM-101. He was advised to correct his low vitamin D3 level and to start using anti-inflammatories such as aspirin, bromelain and low dose Naltrexone. At review one year later a CT scan showed no change and he continued on the regimen. Four years after the diagnosis a CT scan showed that there was a modest but definite progression of the left malignant pleural thickening, and a new right-sided effusion, enlargement of several intrathoracic nodes which had been noted on the early scans. The chest wall lump eventually broke down and required local radiotherapy. He then developed abdominal pain and found to have peritoneal disease. Last year he obtained the
“A 64 year old male heating engineer was investigated for a persistent cough and found to have epithelioid mesothelioma with pleural effusion, lung nodules and increased thoracic lymph nodes. He declined standard of care treatment following his own research and he was enrolled in a named patient programme of IMM-101. He was advised to correct his low vitamin D3 level and to start using anti-inflammatories such as aspirin, bromelain and low dose Naltrexone. At review one year later a CT scan showed no change and he continued on the regimen. Four years after the diagnosis a CT scan showed that there was a modest but definite progression of the left malignant pleural thickening, and a new right-sided effusion, enlargement of several intrathoracic nodes which had been noted on the early scans. The chest wall lump eventually broke down and required local radiotherapy. He then developed abdominal pain and found to have peritoneal disease. Last year he obtained the  “This observational study examined the acute cognitive effects of cannabis.
“This observational study examined the acute cognitive effects of cannabis. “Peripheral neuropathy can significantly impact the quality of life for those who are affected, as therapies from the current treatment algorithm often fail to deliver adequate symptom relief. There has, however, been an increasing body of evidence for the use of cannabinoids in the treatment of chronic, noncancer pain. The efficacy of a topically delivered
“Peripheral neuropathy can significantly impact the quality of life for those who are affected, as therapies from the current treatment algorithm often fail to deliver adequate symptom relief. There has, however, been an increasing body of evidence for the use of cannabinoids in the treatment of chronic, noncancer pain. The efficacy of a topically delivered  “Accumulated evidence indicates that
“Accumulated evidence indicates that  “Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.
“Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial. “Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances.
“Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances. “Available data support the notion that
“Available data support the notion that  “Cannabis sativa L. is a plant long used for its textile fibers, seed oil, and oleoresin with medicinal and psychoactive properties. It is the main source of phytocannabinoids, with over 100 compounds detected so far. In recent years, a lot of attention has been given to the main phytochemicals present in Cannabis sativa L., namely,
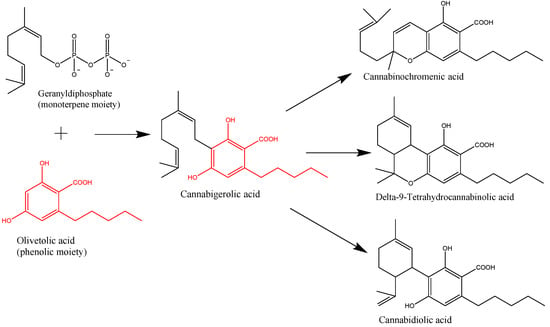
“Cannabis sativa L. is a plant long used for its textile fibers, seed oil, and oleoresin with medicinal and psychoactive properties. It is the main source of phytocannabinoids, with over 100 compounds detected so far. In recent years, a lot of attention has been given to the main phytochemicals present in Cannabis sativa L., namely,