“Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.
“Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.
One of the most promising therapeutic targets for the modulation of immune-inflammatory responses is the endocannabinoid system, particularly the activation of cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2R), a G-protein coupled receptor which mediates the anti-inflammatory properties by modulating numerous signaling pathways. To pharmacologically activate the CB2 receptors, a naturally occurring cannabinoid ligand, beta-caryophyllene (BCP), received attention due to its potent anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and immunomodulatory properties. BCP is recognized as a full selective functional agonist on CB2 receptors and produces therapeutic effects by activating CB2 and the nuclear receptors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs).
BCP is regarded as the first dietary cannabinoid with abundant presence across cannabis and non-cannabis plants, including spices and other edible plants. BCP showed tissue protective properties and favorably modulates numerous signaling pathways and inhibits inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, prostanoids, and eicosanoids. Based on its pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms, and the therapeutic potential of BCP as an immunomodulator, anti-inflammatory, organ-protective, and antiviral, we hypothesize that BCP could be a promising therapeutic and/or preventive candidate to target the triad of infection, immunity, and inflammation in COVID-19. In line with numerous studies that proposed the potential of cannabinoids in COVID-19,
BCP may be a novel candidate compound for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical development due to its unique functional receptor selectivity, wide availability and accessibility, dietary bioavailability, nonpsychoactivity, and negligible toxicity along with druggable properties, including favorable pharmacokinetic and physicochemical properties. Based on reasonable pharmacological mechanisms and therapeutic properties, we speculate that BCP has potential to be investigated against COVID-19 and will inspire further preclinical and clinical studies.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34054510/
“Over the past few months, it has been suggested that modulation of the endocannabinoid system by cannabinoids, including cannabidiol, could be useful in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19 and may improve prognosis. Recently, extract of Cannabis sativa containing phytocannabinoids and terpenes were shown to modulate the inflammatory mediators in alveolar epithelial cells (A549) in COVID-19-associated inflammation and suggested that the phytocannabinoid mix formulation exerted better activity in comparison with individual fractions from cannabis. Many cannabinoids, including cannabidiol, have been suggested for their possible potential as preventive agents or therapeutic adjuvants with other agents in targeting the trinity of infection, inflammation, and immunity in COVID-19.”
“β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a common constitute of the essential oils of numerous spice, food plants and major component in Cannabis.” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23138934
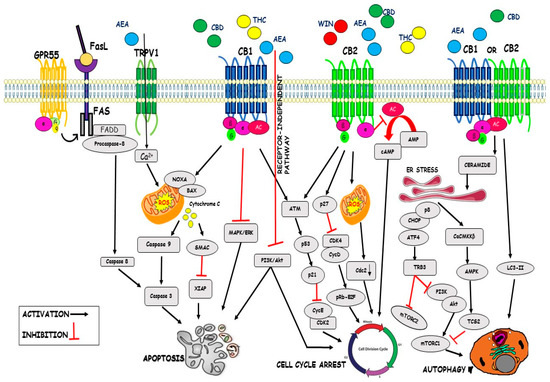
 “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable. 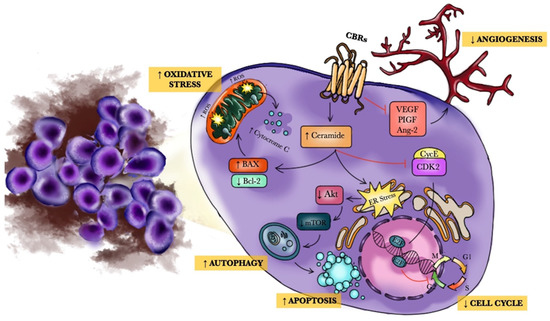

 “Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP).
“Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP).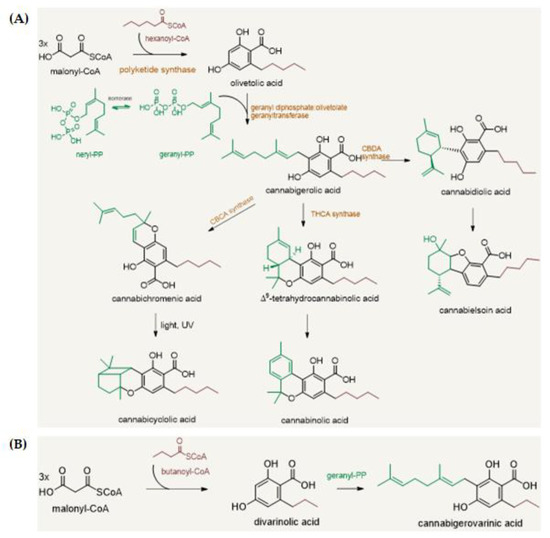
 “The therapeutic potential of
“The therapeutic potential of 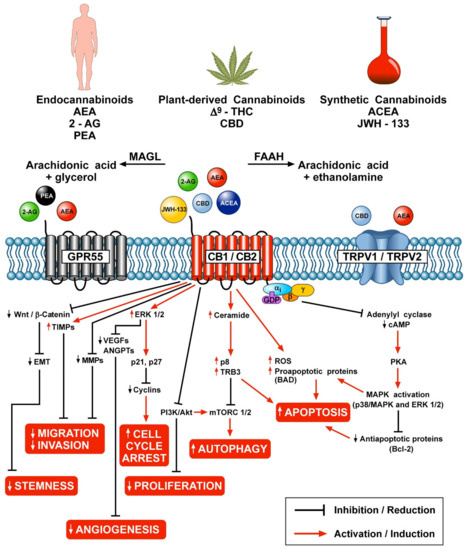
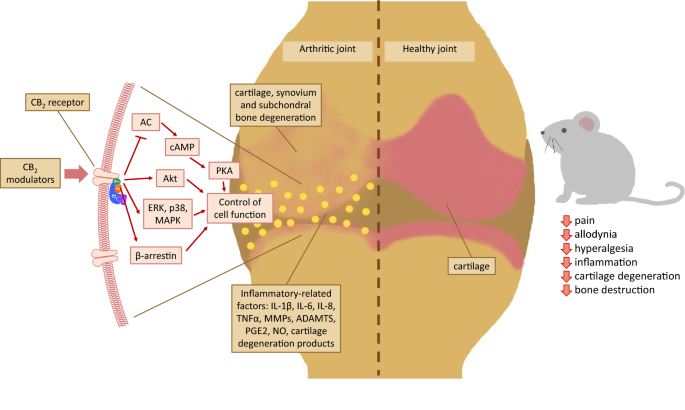 “Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.
“Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.  “Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.
“Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.  “Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.
“Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.  “Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.
“Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.  “Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”
“Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”