 “Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide.
“Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide.
Since the discovery of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as the primary psychoactive component of cannabis over 50 years ago, substantial effort has been directed toward detection of endogenous mediators of cannabinoid activity. The discovery of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol as two endogenous lipid mediators of cannabinoid-like effects (endocannabinoids) has inspired exponential growth in our understanding of this essential pathway, as well as the pathological conditions that result from dysregulated endocannabinoid signaling.
This review examines current knowledge of the endocannabinoid system including metabolic enzymes involved in biosynthesis and degradation and their receptors, and evaluates potential druggable targets for therapeutic intervention.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32894511/
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-030-50621-6_8

 “Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.
“Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.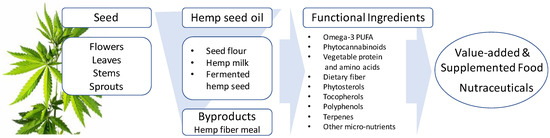
 “Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system.
“Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system. “The compounds present in cannabis have been in use for both recreational and medicinal purposes for many centuries. Changes in the legislation in South Africa have led to an increase in the number of people interested in using these compounds for self-medication. Many of them may approach their general practitioner as the first source of information about possible therapeutic effects. It is important that medical professionals are able to give patients the correct information. Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the main compounds in cannabis plants, and there is evidence that it can successfully treat certain patients with epilepsy. This review looks at the most recent evidence on the use of CBD in the treatment of epilepsy and explores the mechanisms behind these beneficial effects.”
“The compounds present in cannabis have been in use for both recreational and medicinal purposes for many centuries. Changes in the legislation in South Africa have led to an increase in the number of people interested in using these compounds for self-medication. Many of them may approach their general practitioner as the first source of information about possible therapeutic effects. It is important that medical professionals are able to give patients the correct information. Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the main compounds in cannabis plants, and there is evidence that it can successfully treat certain patients with epilepsy. This review looks at the most recent evidence on the use of CBD in the treatment of epilepsy and explores the mechanisms behind these beneficial effects.” “A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.
“A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.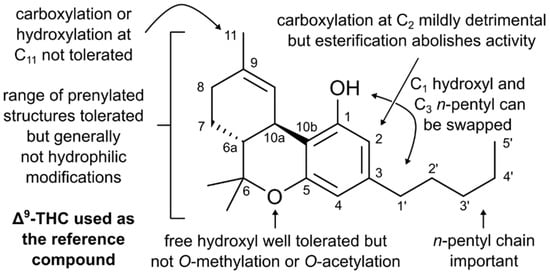
 “Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation.
“Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation. “Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated.
“Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated. “A randomized double-blind clinical trial evaluating the efficacy of a medicinal cannabis formulation (ZTL-101; Zelira Therapeutics Ltd, Perth, Australia) for treating chronic insomnia showed that the therapy is effective and safe.
“A randomized double-blind clinical trial evaluating the efficacy of a medicinal cannabis formulation (ZTL-101; Zelira Therapeutics Ltd, Perth, Australia) for treating chronic insomnia showed that the therapy is effective and safe. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring, non-psychotropic cannabinoid of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa L. and has been known to induce several physiological and pharmacological effects. While CBD is approved as a medicinal product subject to prescription, it is also widely sold over the counter (OTC) in the form of food supplements, cosmetics and electronic cigarette liquids. However, regulatory difficulties arise from its origin being a narcotic plant or its status as an unapproved novel food ingredient.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring, non-psychotropic cannabinoid of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa L. and has been known to induce several physiological and pharmacological effects. While CBD is approved as a medicinal product subject to prescription, it is also widely sold over the counter (OTC) in the form of food supplements, cosmetics and electronic cigarette liquids. However, regulatory difficulties arise from its origin being a narcotic plant or its status as an unapproved novel food ingredient.