 “Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.
Despite anecdotal evidence as an anticancer agent, little is known about the effect CBD has on cancer cells. Given the intractability and poor prognoses of brain cancers in human and veterinary medicine, we sought to characterize the in vitro cytotoxicity of CBD on human and canine gliomas.
Glioma cells treated with CBD showed a range of cytotoxicity from 4.9 to 8.2 μg/ml; canine cells appeared to be more sensitive than human.
These results demonstrate the cytotoxic nature of CBD in human and canine glioma cells and suggest a mechanism of action involving dysregulation of calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial activity.”
“In this present study, we demonstrate that highly purified CBD isolate reduced proliferation and induced caspase-mediated cell death, suggestive of apoptosis, in both canine glioma cell lines SDT3G and J3TBG as well as the human glioma cell lines U87MG and U373MG Uppsala. The growing body of knowledge of the pharmacology, anticancer effects, and other therapeutically relevant properties of cannabidiol reveal the exciting potential of CBD as a potential clinical therapeutic.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.725136/full

 “Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.
“Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.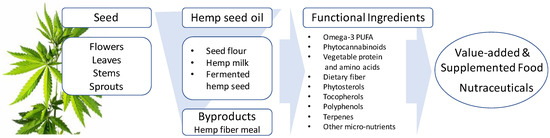
 “Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp. “Hemp (
“Hemp (


