 “Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
“Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
Cardiotoxicity induced by anti-cancer treatments compromise vasospastic and thromboembolic ischemia, dysrhythmia, hypertension, myocarditis, and cardiac dysfunction that can result in heart failure. Importantly, none of the strategies to prevent cardiotoxicity from anticancer therapies is completely safe and satisfactory.
Certain clinically used cardioprotective drugs can even contribute to cancer induction. Since G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are target of forty percent of clinically used drugs, here we discuss the newly identified cardioprotective agents that bind GPCRs of adrenalin, adenosine, melatonin, ghrelin, galanin, apelin, prokineticin and cannabidiol.
We hope to provoke further drug development studies considering these GPCRs as potential targets to be translated to treatment of human heart failure induced by anticancer drugs.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32039239
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2019.00194/full

 “Sleep deprivation (SD) is a common feature in modern society. Prolonged sleep deprivation causes cognition deficits and depression-like behavior in the model of animal experiments.
“Sleep deprivation (SD) is a common feature in modern society. Prolonged sleep deprivation causes cognition deficits and depression-like behavior in the model of animal experiments. “Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
“Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. “Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including
“Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including  “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.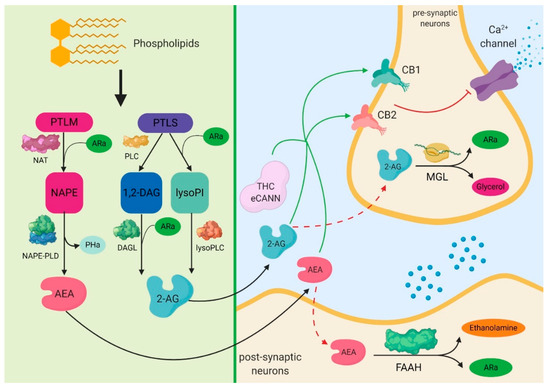
 “Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
“Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
 “Anticholinergic organophosphate (OP) agents act on the diverse serine hydrolases, thereby revealing unexpected biological effects. Epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between OP exposure and development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like symptoms, whereas no plausible mechanism for the OP-induced ADHD has been established.
“Anticholinergic organophosphate (OP) agents act on the diverse serine hydrolases, thereby revealing unexpected biological effects. Epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between OP exposure and development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like symptoms, whereas no plausible mechanism for the OP-induced ADHD has been established. “Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) and even induces remote organ damage.
“Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) and even induces remote organ damage. “Drugs selectively targeting CB2 hold promise for treating neurodegenerative disorders, inflammation, and pain while avoiding psychotropic side effects mediated by CB1. The mechanisms underlying CB2 activation and signaling are poorly understood but critical for drug design. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the human CB2-Gi signaling complex bound to the agonist WIN 55,212-2. The 3D structure reveals the binding mode of WIN 55,212-2 and structural determinants for distinguishing CB2 agonists from antagonists, which are supported by a pair of rationally designed agonist and antagonist. Further structural analyses with computational docking results uncover the differences between CB2 and CB1 in receptor activation, ligand recognition, and Gi coupling. These findings are expected to facilitate rational structure-based discovery of drugs targeting the
“Drugs selectively targeting CB2 hold promise for treating neurodegenerative disorders, inflammation, and pain while avoiding psychotropic side effects mediated by CB1. The mechanisms underlying CB2 activation and signaling are poorly understood but critical for drug design. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the human CB2-Gi signaling complex bound to the agonist WIN 55,212-2. The 3D structure reveals the binding mode of WIN 55,212-2 and structural determinants for distinguishing CB2 agonists from antagonists, which are supported by a pair of rationally designed agonist and antagonist. Further structural analyses with computational docking results uncover the differences between CB2 and CB1 in receptor activation, ligand recognition, and Gi coupling. These findings are expected to facilitate rational structure-based discovery of drugs targeting the