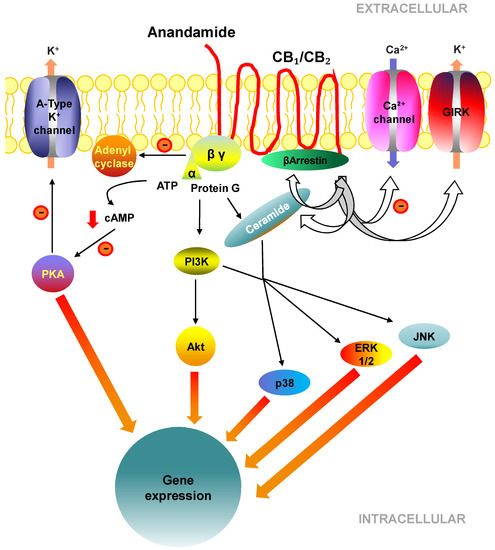
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous cannabinoids are lipid-signalling molecules derived from arachidonic acid involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular dysfunction, portal hypertension, liver fibrosis, and other processes associated with hepatic disease through their interactions with the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Apelin is a peptide that participates in cardiovascular and renal functions, inflammation, angiogenesis, and hepatic fibrosis through its interaction with the APJ receptor. The endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two of the multiple cell-signalling pathways involved in the transformation of quiescent hepatic stellate cells into myofibroblast like cells, the main matrix-producing cells in liver fibrosis. The mechanisms underlying the control of hepatic stellate cell activity are coincident despite the marked dissimilarities between the endocannabinoid and apelin signalling pathways. This review discusses the current understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which the hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems play a significant role in the pathophysiology of liver fibrosis.”
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous cannabinoids are lipid-signalling molecules derived from arachidonic acid involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular dysfunction, portal hypertension, liver fibrosis, and other processes associated with hepatic disease through their interactions with the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Apelin is a peptide that participates in cardiovascular and renal functions, inflammation, angiogenesis, and hepatic fibrosis through its interaction with the APJ receptor. The endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two of the multiple cell-signalling pathways involved in the transformation of quiescent hepatic stellate cells into myofibroblast like cells, the main matrix-producing cells in liver fibrosis. The mechanisms underlying the control of hepatic stellate cell activity are coincident despite the marked dissimilarities between the endocannabinoid and apelin signalling pathways. This review discusses the current understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which the hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems play a significant role in the pathophysiology of liver fibrosis.”
Category Archives: Liver Disease
Cannabinoid receptor 1 knockout alleviates hepatic steatosis by downregulating perilipin 2.
With the current study we aimed to verify the modulatory effect of endocannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1)-signaling on perilipin 2 (PLIN2)-mediated lipophagy.
In conclusion, these results suggest that loss of CB1 signaling leads to reduced PLIN2 abundance, which triggers lipophagy. Our new findings about the association between CB1 signaling and PLIN2 may stimulate translational studies analyzing new diagnostic and therapeutic options for NAFLD.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31570772
“In conclusion, we demonstrated that the CB1 receptor knockout in vivo and pharmacologic antagonization of CB1 in cell culture decreased PLIN2 expression, which might be an essential step in lipid breakdown. Thus, pharmacologic modulation of the CB1-PLIN2 axis might represent a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of steatosis.”
Cannabidiol improves metabolic dysfunction in middle-aged diabetic rats submitted to a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a compound obtained from Cannabis sativa, has wide range of therapeutic properties, including mitigation of diabetes and neurodegeneration.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a compound obtained from Cannabis sativa, has wide range of therapeutic properties, including mitigation of diabetes and neurodegeneration.
Cerebral ischemia and consequent learning disabilities are aggravated in elderly diabetic subjects. However, there are no studies showing the effect of CBD treatment in elderly diabetes patients suffering cerebral ischemia.
The present work tested the hypothesis that CBD treatment improves metabolic dysfunctions in middle-aged diabetic rats submitted to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
CBD may be used as therapeutic tool to protect metabolism against injuries from diabetes aggravated by cerebral ischemia.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31499052
“CBD reduced hyperglycemia of middle-aged diabetic rats with CCH. CBD increased insulin secretion and decreased AGEs levels. CBD reduced fructosamine, LDL, HDL, triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. CBD presented hepatoprotective effect. CBD could mitigate neurodegeneration caused by DM associated to cerebral ischemia.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S000927971930701X?via%3Dihub
Interplay of liver-heart inflammatory axis and cannabinoid 2 receptor signalling in an experimental model of hepatic cardiomyopathy.
 “Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective cannabinoid-2 receptor (CB2 -R) agonist, known to attenuate inflammation and fibrosis, was used to explore the impact of liver inflammation, fibrosis on cardiac function.
“Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective cannabinoid-2 receptor (CB2 -R) agonist, known to attenuate inflammation and fibrosis, was used to explore the impact of liver inflammation, fibrosis on cardiac function.
MAIN RESULTS:
BDL induced massive inflammation (increased leukocyte infiltration, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines), oxidative stress, microvascular dysfunction, and fibrosis in the liver. These pathological changes were accompanied by impaired diastolic, systolic and macrovascular functions, cardiac inflammation (increased MIP1, interleukin-1, P-selectin, CD45+ cells) and oxidative stress (increased malondialdehyde, 3-nitrotyrosine and NADPH-oxidases). CB2 -R up-regulation was observed both in livers and hearts of mice exposed to BDL. CB2 -R activation markedly improved hepatic inflammation, impaired microcirculation, fibrosis. CB2 -R activation also decreased serum TNF-alpha levels, and improved cardiac dysfunction, myocardial inflammation and oxidative stress underlining the importance of inflammatory mediators in the pathology of hepatic cardiomyopathy.
CONCLUSION:
We propose BDL-induced cardiomyopathy in mice as a model for hepatic/cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. This cardiomyopathy, similarly to cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in humans, is characterized by systemic hypotension, impaired macro- and microvascular function accompanied by both systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Our results indicate that the liver-heart inflammatory axis has a pivotal pathophysiological role in the development of hepatic cardiomyopathy. Thus, controlling liver and/or myocardial inflammation (e.g. with selective CB2-R agonists) may delay/prevent the development of cardiomyopathy in severe liver disease. ”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31469200
https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/hep.30916
Cannabinoid receptor-1 antagonism: a new perspective on treating a murine schistosomal liver fibrosis model.
 “Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF.
“Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF.
The role of the cannabinoid (CB) receptor family in liver fibrosis has recently been highlighted.
This study aimed to assess the therapeutic effect of CB1 receptor antagonism in reversing SSLF in a murine model of Schistosoma mansoni infection.
MAIN CONCLUSIONS:
Combining PZQ with CB1 receptor antagonists yielded the best results in reversing SSLF. To our knowledge, this is the first study to test this regimen in S. mansoni infection.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31389521
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0074-02762019000100338&tlng=en
Potential Mechanisms Influencing the Inverse Relationship Between Cannabis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Commentary.
“Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) develops when the liver is unable to oxidize or export excess free fatty acids generated by adipose tissue lipolysis, de novo lipogenesis, or dietary intake. Although treatment has generally been centered on reversing metabolic risk factors that increase the likelihood of NAFLD by influencing lifestyle modifications, therapeutic modalities are being studied at the cellular and molecular level.
The endocannabinoid system has been of recent focus. The agonism and antagonism of cannabinoid receptors play roles in biochemical mechanisms involved in the development or regression of NAFLD. Exocannabinoids and endocannabinoids, the ligands which bind cannabinoid receptors, have been studied in this regard.
Exocannabinoids found in cannabis (marijuana) may have a therapeutic benefit. Our recent study demonstrated an inverse association between marijuana use and NAFLD among adults in the United States.
This commentary combines knowledge on the role of the endocannabinoid system in the setting of NAFLD with the findings in our article to hypothesize different potential mechanisms that may influence the inverse relationship between cannabis and NAFLD.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31308686
Cannabis consumption and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A three years longitudinal study in first episode non-affective psychosis patients.
 “Increased incidence of obesity and excess weight lead to an increased incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent evidence indicates a protective effect of cannabis consumption on weight gain and related metabolic alterations in psychosis patients. Overall, patients are at greater risk of presenting fatty diseases, such as NAFLD, partly due to lipid and glycemic metabolic disturbances. However, there are no previous studies on the likely effect of cannabis on liver steatosis. We aimed to explore if cannabis consumption had an effect on hepatic steatosis, in a sample of first-episode (FEP) non-affective psychosis.
“Increased incidence of obesity and excess weight lead to an increased incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent evidence indicates a protective effect of cannabis consumption on weight gain and related metabolic alterations in psychosis patients. Overall, patients are at greater risk of presenting fatty diseases, such as NAFLD, partly due to lipid and glycemic metabolic disturbances. However, there are no previous studies on the likely effect of cannabis on liver steatosis. We aimed to explore if cannabis consumption had an effect on hepatic steatosis, in a sample of first-episode (FEP) non-affective psychosis.
RESULTS:
At 3-year follow-up, cannabis users presented significantly lower FLI scores than non-users (F = 13.874; p < .001). Moreover, cannabis users less frequently met the criteria for liver steatosis than non-users (X2 = 7.97, p = .019). Longitudinally, patients maintaining cannabis consumption after 3 years presented the smallest increment in FLI over time, which was significantly smaller than the increment in FLI presented by discontinuers (p = .022) and never-users (p = .016). No differences were seen in fibrosis scores associated with cannabis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Cannabis consumption may produce a protective effect against liver steatosis in psychosis, probably through the modulation of antipsychotic-induced weight gain.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31228640
“Cannabis consumption is associated with a lower risk of liver steatosis in psychosis. Cannabis use is not associated with liver fibrosis.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278584619301393?via%3Dihub
Endocannabinoid System in Hepatic Glucose Metabolism, Fatty Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis.

“There is growing evidence that glucose metabolism in the liver is in part under the control of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) which is also supported by its presence in this organ. The ECS consists of its cannabinoid receptors (CBRs) and enzymes that are responsible for endocannabinoid production and metabolism. ECS is known to be differentially influenced by the hepatic glucose metabolism and insulin resistance, e.g., cannabinoid receptor type 1(CB1) antagonist can improve the glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. Interestingly, our own study shows that expression patterns of CBRs are influenced by the light/dark cycle, which is of significant physiological and clinical interest. The ECS system is highly upregulated during chronic liver disease and a growing number of studies suggest a mechanistic and therapeutic impact of ECS on the development of liver fibrosis, especially putting its receptors into focus. An opposing effect of the CBRs was exerted via the CB1 or CB2 receptor stimulation. An activation of CB1promoted fibrogenesis, while CB2 activation improved antifibrogenic responses. However, underlying mechanisms are not yet clear. In the context of liver diseases, the ECS is considered as a possible mediator, which seems to be involved in the synthesis of fibrotic tissue, increase of intrahepatic vascular resistance and subsequently development of portal hypertension. Portal hypertension is the main event that leads to complications of the disease. The main complication is the development of variceal bleeding and ascites, which have prognostic relevance for the patients. The present review summarizes the current understanding and impact of the ECS on glucose metabolism in the liver, in association with the development of liver cirrhosis and hemodynamics in cirrhosis and its complication, to give perspectives for development of new therapeutic strategies.”
Effects of cannabidiol on alcohol-related outcomes: A review of preclinical and human research.

“This article reviews preclinical and human studies examining the effects of CBD administration on alcohol responses. Preliminary preclinical results suggest that CBD can attenuate alcohol consumption and potentially protect against certain harmful effects of alcohol, such as liver and brain damage.”
Therapeutic prospects of cannabidiol for alcohol use disorder and alcohol-related damages on the liver and the brain
 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a natural compound of cannabis, which exerts complex and widespread immunomodulatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic, and antiepileptic properties. Many experimental data suggest that CBD could have several types of application in alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol-related damage on the brain and the liver.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a natural compound of cannabis, which exerts complex and widespread immunomodulatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic, and antiepileptic properties. Many experimental data suggest that CBD could have several types of application in alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol-related damage on the brain and the liver.
Experimental studies converge to find that CBD reduces the overall level of alcohol drinking in animal models of AUD by reducing ethanol intake, motivation for ethanol, relapse, and by decreasing anxiety and impulsivity. Moreover, CBD has been shown to reduce alcohol-related steatosis and fibrosis in the liver by reducing lipid accumulation, stimulating autophagy, modulating inflammation, reducing oxidative stress, and inducing death of activated hepatic stellate cells. Last, CBD has been found to reduce alcohol-related brain damage, preventing neuronal loss by its antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties.
CBD could directly reduce alcohol drinking in subjects with AUD. But other original applications warrant human trials in this population. By reducing alcohol-related processes of steatosis in the liver, and brain alcohol-related damage, CBD could improve both the hepatic and neurocognitive outcomes of subjects with AUD, regardless of the individual drinking trajectories. This might pave the way for testing new harm reduction approaches in AUD, i.e., for protecting the organs of subjects with an ongoing AUD.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2019.00627/abstract