 “For patients with chronic, non-cancer pain, traditional pain-relieving medications include opioids, which have shown benefits but are associated with increased risks of addiction and adverse effects.
“For patients with chronic, non-cancer pain, traditional pain-relieving medications include opioids, which have shown benefits but are associated with increased risks of addiction and adverse effects.
Medical cannabis has emerged as a treatment alternative for managing these patients and there has been a rise in the number of randomized clinical trials in recent years; therefore, a systematic review of the evidence was warranted.
RESULTS:
Thirty-six trials (4006 participants) were included, examining smoked cannabis (4 trials), oromucosal cannabis sprays (14 trials), and oral cannabinoids (18 trials). Compared with placebo, cannabinoids showed a significant reduction in pain which was greatest with treatment duration of 2 to 8 weeks (weighted mean difference on a 0-10 pain visual analogue scale -0.68, 95% confidence interval [CI], -0.96 to -0.40, I 2 = 8%, P < .00001; n = 16 trials). When stratified by route of administration, pain condition, and type of cannabinoids, oral cannabinoids had a larger reduction in pain compared with placebo relative to oromucosal and smoked formulations but the difference was not significant (P[interaction] > .05 in all the 3 durations of treatment); cannabinoids had a smaller reduction in pain due to multiple sclerosis compared with placebo relative to other neuropathic pain (P[interaction] = .05) within 2 weeks and the difference was not significant relative to pain due to rheumatic arthritis; nabilone had a greater reduction in pain compared with placebo relative to other types of cannabinoids longer than 2 weeks of treatment but the difference was not significant (P[interaction] > .05). Serious AEs were rare, and similar across the cannabinoid (74 out of 2176, 3.4%) and placebo groups (53 out of 1640, 3.2%). There was an increased risk of non-serious AEs with cannabinoids compared with placebo.
CONCLUSIONS:
There was moderate evidence to support cannabinoids in treating chronic, non-cancer pain at 2 weeks. Similar results were observed at later time points, but the confidence in effect is low. There is little evidence that cannabinoids increase the risk of experiencing serious AEs, although non-serious AEs may be common in the short-term period following use.”

 “For many centuries,
“For many centuries,  “While medical and recreational cannabis use is becoming more frequent among older adults, the neurocognitive consequences of cannabis use in this age group are unclear. The aim of this literature review was to synthesize and evaluate the current knowledge on the association of cannabis use during older-adulthood with cognitive function and brain aging.
“While medical and recreational cannabis use is becoming more frequent among older adults, the neurocognitive consequences of cannabis use in this age group are unclear. The aim of this literature review was to synthesize and evaluate the current knowledge on the association of cannabis use during older-adulthood with cognitive function and brain aging. “Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system, mediate brain homeostasis by controlling neuronal proliferation/differentiation and synaptic activity. In response to external signals from neuropathological conditions, homeostatic (M0) microglia can adopt one of two activation states: the classical (M1) activation state, which secretes mediators of the proinflammatory response, and the alternative (M2) activation state, which presumably mediates the resolution of neuroinflammation and tissue repair/remodeling.
“Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system, mediate brain homeostasis by controlling neuronal proliferation/differentiation and synaptic activity. In response to external signals from neuropathological conditions, homeostatic (M0) microglia can adopt one of two activation states: the classical (M1) activation state, which secretes mediators of the proinflammatory response, and the alternative (M2) activation state, which presumably mediates the resolution of neuroinflammation and tissue repair/remodeling.
 “Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).
“Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).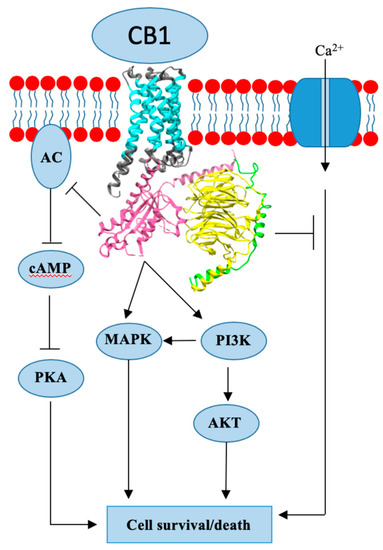
 “Herein, 11 general types of natural cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa as well as 50 (-)-CBD analogues with therapeutic potential were described. The underlying molecular mechanisms of CBD as a therapeutic candidate for epilepsy and neurodegenerative diseases were comprehensively clarified. CBD indirectly acts as an endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist to exert its neuroprotective effects. CBD also promotes neuroprotection through different signal transduction pathways mediated indirectly by cannabinoid receptors. Furthermore, CBD prevents the glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) hyperphosphorylation caused by Aβ and may be developed as a new therapeutic candidate for Alzheimer’s disease.”
“Herein, 11 general types of natural cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa as well as 50 (-)-CBD analogues with therapeutic potential were described. The underlying molecular mechanisms of CBD as a therapeutic candidate for epilepsy and neurodegenerative diseases were comprehensively clarified. CBD indirectly acts as an endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist to exert its neuroprotective effects. CBD also promotes neuroprotection through different signal transduction pathways mediated indirectly by cannabinoid receptors. Furthermore, CBD prevents the glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) hyperphosphorylation caused by Aβ and may be developed as a new therapeutic candidate for Alzheimer’s disease.”
 “The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable.
“The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable. “Medicinal
“Medicinal