“Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities.
“Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities.
Certain marijuana components, namely the non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and psychoactive tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), are defined as immunomodulators.9 We test whether two sources of stem cells, primed with CBD or THC, would demonstrate improved regenerative abilities.
Human adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) and bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMDSCs), not obtained from the same individual, were treated with low (300 nM) or high (3 μM) concentration CBD. Porcine ASCs and BMDSCs were isolated from a single pig, and treated with either low or high concentrations of CBD or THC. Transwell migration and MTT proliferation assays were performed on the human ASCs and BMDSCs. Also, transwell migration assay was performed on the porcine ASCs and BMDSCs. Finally, a wound healing scratch assay in porcine primary fibroblasts (PFs) was performed, co-cultured with the cannabinoid-treated ASCs.
CBD priming at low concentration induces migration by 180% (P < .01) in porcine ASCs, and by only 93% (P < .02) in porcine BMDSCs. In porcine stem cells, THC priming at low concentration induces migration by 91.6% (P < .01) in ASCs but by only 44.3% (P < .03) in BMDSCs. Compared to PFs co-cultured with untreated ASCs, PFs co-cultured with low CBD-primed ASCs had 75% faster wound closure at 18 hours (P < .01).
CBD and THC priming of ASCs and BMDSCs, particularly at lower doses, enhances a number of regenerative parameters, suggesting that these major marijuana components may improve stem cell-based therapies.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY: Our study demonstrates that cannabinoids can enhance the regenerative capacity of two major sources of stem cells, adipose- and bone marrow-derived, from human and porcine donors. Stem cell isolation and expansion is invasive, costly and time consuming. Stem cells with improved regenerative properties may be effective in the treatment of acute or chronic wounds. This is the first study to compare the priming potential of two sources of stem cells from the same animal, with the same genetic and epigenetic profile, as well as the first to prime with THC.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33349985/
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbf.3609


 “Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.”
“Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.” “Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer.
“Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most popular emerging plant extracts that is being investigated for its wide range of potential health benefits.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most popular emerging plant extracts that is being investigated for its wide range of potential health benefits. “Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.
“Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.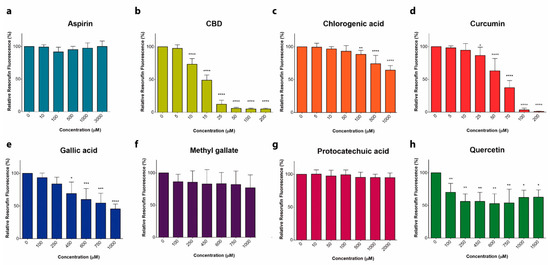
 “Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities.
“Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities. “Effective treatment choices to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) are limited because of the absence of effective target-based therapeutics. The main object of the current research was to estimate the antiviral activity of cannabinoids (CBDs) against the human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.
“Effective treatment choices to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) are limited because of the absence of effective target-based therapeutics. The main object of the current research was to estimate the antiviral activity of cannabinoids (CBDs) against the human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.
 “Cannabis sativa is a well-known plant which has been of benefit since ancient times in several medicinal systems, including Chinese, Indian, Greek and Egyptian ones.
“Cannabis sativa is a well-known plant which has been of benefit since ancient times in several medicinal systems, including Chinese, Indian, Greek and Egyptian ones. “In the last decade the use of medical cannabis (MC) for palliative cancer treatment has risen. However, the choice between products is arbitrary and most patients are using Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-dominant cannabis products.
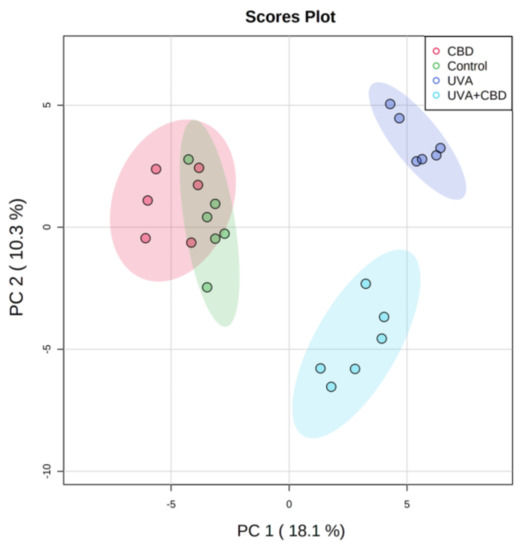
“In the last decade the use of medical cannabis (MC) for palliative cancer treatment has risen. However, the choice between products is arbitrary and most patients are using Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-dominant cannabis products. “UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
“UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.