 “In vivo studies show that cannabidiol (CBD) acutely reduces blood pressure (BP) in men.
“In vivo studies show that cannabidiol (CBD) acutely reduces blood pressure (BP) in men.
The aim of this study was to assess the effects of repeated CBD dosing on haemodynamics.
RESULTS:
Compared to placebo, CBD significantly reduced resting mean arterial pressure (P = .04, two-way ANOVA, mean difference (MD) -2 mmHg, 95% CI -3.6 to -0.3) after acute dosing, but not after repeated dosing. In response to stress, volunteers who had taken CBD had lower systolic BP after acute (P = .001, two-way ANOVA, MD -6 mmHg, 95% CI -10 to -1) and repeated (P = .02, two-way ANOVA, MD -5.7 mmHg, 95% CI -10 to -1) dosing. Seven days of CBD increased internal carotid artery diameter (MD +0.55 mm, P = .01). Within the CBD group, repeated dosing reduced arterial stiffness by day 7 (pulse wave velocity; MD -0.44 m/s, P = .05) and improved endothelial function (flow mediation dilatation, MD +3.5%, P = .02, n = 6 per group), compared to day 1.
CONCLUSION:
CBD reduces BP at rest after a single dose but the effect is lost after seven days of treatment (tolerance); however, BP reduction during stress persists. The reduction in arterial stiffness and improvements in endothelial function after repeated CBD dosing are findings that warrant further investigation in populations with vascular diseases.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32128848
https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/bcp.14225

 “To assess any clinical improvement attributable to the addition of medical
“To assess any clinical improvement attributable to the addition of medical  “Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).
“Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).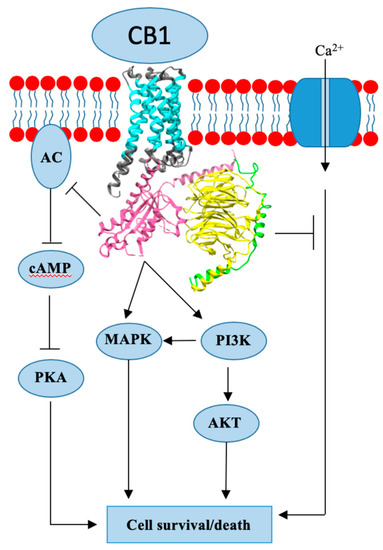
 “Clinical evidence supports effectiveness of
“Clinical evidence supports effectiveness of  “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and pathologically by the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau hyperphosphorylation causing neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Current AD treatments do not stop or reverse the disease progression, highlighting the need for more effective therapeutics.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and pathologically by the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau hyperphosphorylation causing neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Current AD treatments do not stop or reverse the disease progression, highlighting the need for more effective therapeutics.
 “The growing interest in cannabidiol (CBD), specifically a pure form of CBD, as a treatment for epilepsy, among other conditions, is reflected in recent changes in legislation in some countries.
“The growing interest in cannabidiol (CBD), specifically a pure form of CBD, as a treatment for epilepsy, among other conditions, is reflected in recent changes in legislation in some countries. “Marijuana is increasingly utilized for the treatment of multiple medical problems, including back pain, in the United States. Although there is strong preclinical evidence supporting the promise of
“Marijuana is increasingly utilized for the treatment of multiple medical problems, including back pain, in the United States. Although there is strong preclinical evidence supporting the promise of  “Neuropathic pain conditions including neuropathic orofacial pain (NOP) are difficult to treat. Contemporary therapeutic agents for neuropathic pain are often ineffective in relieving pain and are associated with various adverse effects. Finding new options for treating neuropathic pain is a major priority in pain-related research.
“Neuropathic pain conditions including neuropathic orofacial pain (NOP) are difficult to treat. Contemporary therapeutic agents for neuropathic pain are often ineffective in relieving pain and are associated with various adverse effects. Finding new options for treating neuropathic pain is a major priority in pain-related research. “The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.
“The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.