The effects of the active compound of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), on gut motility and tone have been studied in several experimental models. It is unknown whether these effects correlate with improved healthcare utilization among cannabis users.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact of cannabis use on inpatient length of stay and resource utilization for patients with a primary discharge diagnosis of IBS.
Cannabis users were less likely to have the following: upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (17.9% vs. 26.1%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 0.51 [0.36 to 0.73]; p<0.001) and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy (21.1% vs. 28.7%; aOR: 0.54 [0.39 to 0.75]; p<0.001). Additionally, cannabis users had shorter length of stay (2.8 days vs. 3.6 days; p=0.004) and less total charges (US$20,388 vs. US$23,624). There was no difference in the frequency of CT abdomen performed.
Cannabis use may decrease inpatient healthcare utilization in IBS patients. These effects could possibly be through the effect of cannabis on the endocannabinoid system.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32528750/
“Our study provides evidence to suggest that cannabis use may decrease healthcare utilization and costs among hospitalized patients with IBS. These findings are likely attributable to the effects of cannabis’ active compound, THC, on gastrointestinal motility and colonic compliance. The role of cannabis in the treatment for IBS has potential for significant impact at the individual and population level given the burden of IBS on individual quality of life and healthcare expenditures.”

 “Growing evidence recognises cannabinoid receptors as potential therapeutic targets for pain. Consequently, there is increasing interest in developing cannabinoid receptor agonists for treating pain.
“Growing evidence recognises cannabinoid receptors as potential therapeutic targets for pain. Consequently, there is increasing interest in developing cannabinoid receptor agonists for treating pain. “Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options.
“Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options. “Δ9‐THCA‐A, the precursor of Δ9‐THC, is a non‐psychotropic phytocannabinoid that shows PPARγ agonistic activity. Herein, we investigated Δ9‐THCA ability to modulate classic cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and evaluated its anti‐arthritis activity.
“Δ9‐THCA‐A, the precursor of Δ9‐THC, is a non‐psychotropic phytocannabinoid that shows PPARγ agonistic activity. Herein, we investigated Δ9‐THCA ability to modulate classic cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and evaluated its anti‐arthritis activity.
 “Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by aberrant bone marrow plasma cell (PC) proliferation and is one of the most common hematological malignancies. The potential effect of cannabinoids on the immune system and hematological malignancies has been poorly characterized.
“Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by aberrant bone marrow plasma cell (PC) proliferation and is one of the most common hematological malignancies. The potential effect of cannabinoids on the immune system and hematological malignancies has been poorly characterized.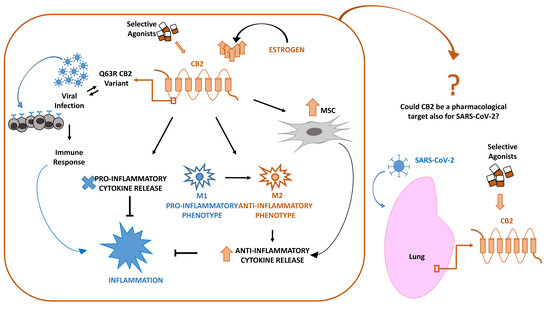
 “Historical relevance: Cannabis sativa L. (C. sativa) is a plant whose use as a therapeutic agent shares its origins with the first Far East’s human societies. Cannabis has been used not only for recreational purposes, but as a food to obtain textile fibers, to produce hemp paper, to treat many physical and mental disorders.
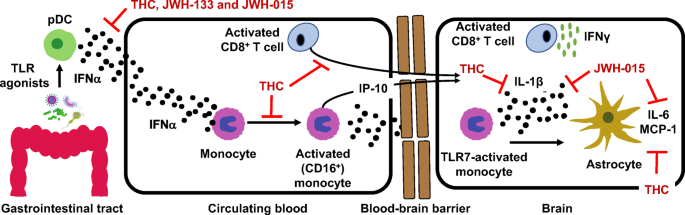
“Historical relevance: Cannabis sativa L. (C. sativa) is a plant whose use as a therapeutic agent shares its origins with the first Far East’s human societies. Cannabis has been used not only for recreational purposes, but as a food to obtain textile fibers, to produce hemp paper, to treat many physical and mental disorders. “HIV infection affects an estimated 38 million people. Approximately 50% of HIV patients exhibit neurocognitive dysfunction termed HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). HAND is a consequence of chronic low-level neuroinflammation due to HIV entry into the brain. Initially, monocytes become activated in circulation and traffic to the brain. Monocytes, when activated, become susceptible to infection by HIV and can then carry the virus across the blood brain barrier. Once in the brain, activated monocytes secrete chemokines, which recruit virus-specific CD8+ T cells into the brain to further promote neuroinflammation. HAND is closely linked to systemic inflammation driven, in part, by HIV but is also due to persistent translocation of microorganisms across the GI tract. Persistent anti-viral responses in the GI tract compromise microbial barrier integrity. Indeed, HIV patients can exhibit remarkably high levels of activated (CD16+) monocytes in circulation.
“HIV infection affects an estimated 38 million people. Approximately 50% of HIV patients exhibit neurocognitive dysfunction termed HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). HAND is a consequence of chronic low-level neuroinflammation due to HIV entry into the brain. Initially, monocytes become activated in circulation and traffic to the brain. Monocytes, when activated, become susceptible to infection by HIV and can then carry the virus across the blood brain barrier. Once in the brain, activated monocytes secrete chemokines, which recruit virus-specific CD8+ T cells into the brain to further promote neuroinflammation. HAND is closely linked to systemic inflammation driven, in part, by HIV but is also due to persistent translocation of microorganisms across the GI tract. Persistent anti-viral responses in the GI tract compromise microbial barrier integrity. Indeed, HIV patients can exhibit remarkably high levels of activated (CD16+) monocytes in circulation.