 “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of cannabinoids in animal models of GBM have been described, but the diversity of experimental conditions and of outcomes hindered definitive conclusions about cannabinoids efficacy.
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of cannabinoids in animal models of GBM have been described, but the diversity of experimental conditions and of outcomes hindered definitive conclusions about cannabinoids efficacy.
A search in different databases (Pubmed, Web of Science, Scopus and SciELO) was conducted during June 2019 to systematically identify publications evaluating the effects of cannabinoids in murine xenografts models of GBM. The tumour volume and number of animals were extracted, being a random effects meta-analysis of these results performed to estimate the efficacy of cannabinoids. The impact of different experimental factors and publication bias on the efficacy of cannabinoids was also assessed. Nine publications, which satisfied the inclusion criteria, were identified and subdivided in 22 studies involving 301 animals.
Overall, cannabinoid therapy reduced the fold of increase in tumour volume in animal models of GBM, when compared with untreated controls. The overall weighted standardized difference in means (WSDM) for the effect of cannabinoids was -1.399 (95% CI: -1.900 to -0.898; P-value<0.0001). Furthermore, treatment efficacy was observed for different types of cannabinoids, alone or in combination, and for different treatment durations.
Cannabinoid therapy was still effective after correcting for publication bias. The results indicate that cannabinoids reduce the tumour growth in animal models of GBM, even after accounting for publication bias.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32145324
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299920301473?via%3Dihub
 “Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) is a rare and challenging cause of pediatric intestinal failure, requiring long-term parenteral nutrition in most cases. Despite optimal management, some patients experience chronic abdominal pain and recurrent obstructive episodes with a major impact on their quality of life.
“Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) is a rare and challenging cause of pediatric intestinal failure, requiring long-term parenteral nutrition in most cases. Despite optimal management, some patients experience chronic abdominal pain and recurrent obstructive episodes with a major impact on their quality of life.
 “Excessive fear and anxiety, coupled with corticolimbic dysfunction, are core features of stress- and trauma-related psychopathology, such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
“Excessive fear and anxiety, coupled with corticolimbic dysfunction, are core features of stress- and trauma-related psychopathology, such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
 “Cannabis use among inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients is common. There are many studies of various laboratory models demonstrating the anti-inflammatory effect of cannabis, but their translation to human disease is still lacking.
“Cannabis use among inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients is common. There are many studies of various laboratory models demonstrating the anti-inflammatory effect of cannabis, but their translation to human disease is still lacking. “Given the infancy and evolving complexity of medicinal marijuana, an evolving political landscape, and the growing frequency of its use in cancer care, it is important for oncologists to be actively engaged in developing and successfully implementing clinical trials focusing on medical marijuana.
“Given the infancy and evolving complexity of medicinal marijuana, an evolving political landscape, and the growing frequency of its use in cancer care, it is important for oncologists to be actively engaged in developing and successfully implementing clinical trials focusing on medical marijuana. “Ratios of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and
“Ratios of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and  “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of  “Phytocannabinoids (pCBs) are a large family of meroterpenoids isolated from the plant Cannabis sativa. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the best investigated phytocannabinoids due to their relative abundance and interesting bioactivity profiles. In addition to various targets, THC and CBD are also well-known agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor involved in energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. In the search of new pCBs potentially acting as PPARγ agonists, we identified cannabimovone (CBM), a structurally unique abeo-menthane pCB, as a novel PPARγ modulator via a combined computational and experimental approach. The ability of CBM to act as dual PPARγ/α agonist was also evaluated. Computational studies suggested a different binding mode toward the two isoforms, with the compound able to recapitulate the pattern of H-bonds of a canonical agonist only in the case of PPARγ. Luciferase assays confirmed the computational results, showing a selective activation of PPARγ by CBM in the low micromolar range. CBM promoted the expression of PPARγ target genes regulating the adipocyte differentiation and prevented palmitate-induced insulin signaling impairment. Altogether, these results candidate CBM as a novel bioactive compound potentially useful for the treatment of insulin resistance-related disorders.”
“Phytocannabinoids (pCBs) are a large family of meroterpenoids isolated from the plant Cannabis sativa. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the best investigated phytocannabinoids due to their relative abundance and interesting bioactivity profiles. In addition to various targets, THC and CBD are also well-known agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor involved in energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. In the search of new pCBs potentially acting as PPARγ agonists, we identified cannabimovone (CBM), a structurally unique abeo-menthane pCB, as a novel PPARγ modulator via a combined computational and experimental approach. The ability of CBM to act as dual PPARγ/α agonist was also evaluated. Computational studies suggested a different binding mode toward the two isoforms, with the compound able to recapitulate the pattern of H-bonds of a canonical agonist only in the case of PPARγ. Luciferase assays confirmed the computational results, showing a selective activation of PPARγ by CBM in the low micromolar range. CBM promoted the expression of PPARγ target genes regulating the adipocyte differentiation and prevented palmitate-induced insulin signaling impairment. Altogether, these results candidate CBM as a novel bioactive compound potentially useful for the treatment of insulin resistance-related disorders.”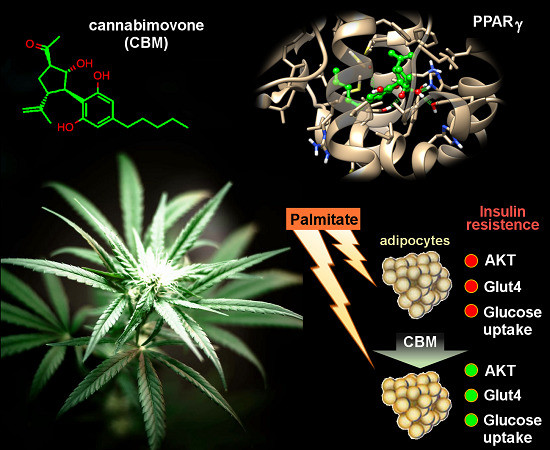
 “Over the past decade, patients, families, and medical cannabis advocates have campaigned in many countries to allow patients to use cannabis preparations to treat the symptoms of serious illnesses that have not responded to conventional treatment.
“Over the past decade, patients, families, and medical cannabis advocates have campaigned in many countries to allow patients to use cannabis preparations to treat the symptoms of serious illnesses that have not responded to conventional treatment.