 “Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.
“Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.
Objectives: To clarify the role of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol(THC):cannabidiol(CBD) oromucosal spray, coupled to robot-aided gait training (RAGT) using the Lokomat©Pro to improve functional ambulation in patients with MS.
Methods: We compared 20 patients with MS, who were treated with THC:CBD oromucosal spray in add-on to the ongoing oral antispastic therapy (OAT) (group A), with 20 individuals with MS (matched for clinical-demographic characteristics) who were treated only with OAT (group B). Both the groups underwent RAGT using the Lokomat-Pro (three 45-minute sessions per week). Our primary outcome measures were the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) and the 10 meters walking test (10MWT). As secondary outcome measures we evaluated the brain cortical excitability by using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Both parameters were taken before and after the end of the RAGT.
Results: FIM improved in group A more than in group B (p<0.001). Moreover, 10MWT decreased in group A more than in group B (p<0.001). These clinical findings were paralleled by a more evident reshape of intracortical excitability in both upper and lower limbs, as suggested by motor evoked potential amplitude increase (p<0.001), intracortical inhibition strengthening (p<0.001), and intracortical facilitation decrease (p=0.01) in group A as compared to group B.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the combined THC:CBD-RAGT approach could be useful in improving gait performance in patients with MS.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32447249/
“The coupled therapy is preliminarily demonstrated as safe and efficacious.”
https://www.msard-journal.com/article/S2211-0348(20)30253-4/pdf
 “Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes.
“Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes.
 “Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
“Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS). “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Moderate to severe spasticity is commonly reported in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and its management is still a challenge. Cannabinoids were recently suggested as add-on therapy for the treatment of spasticity and chronic pain in MS but there is no conclusive scientific evidence on their safety, especially on cognition and over long periods.
“Moderate to severe spasticity is commonly reported in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and its management is still a challenge. Cannabinoids were recently suggested as add-on therapy for the treatment of spasticity and chronic pain in MS but there is no conclusive scientific evidence on their safety, especially on cognition and over long periods. “Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.
“Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.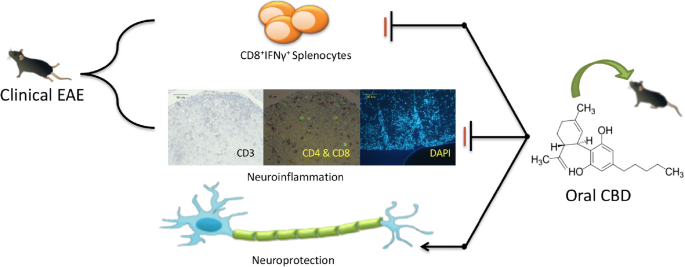
 “The pathophysiological relevance of the endocannabinoid system has been widely demonstrated in a variety of diseases including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic issues. Therefore, targeting the receptors and the endogenous machinery involved in this system can provide a successful therapeutic outcome.
“The pathophysiological relevance of the endocannabinoid system has been widely demonstrated in a variety of diseases including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic issues. Therefore, targeting the receptors and the endogenous machinery involved in this system can provide a successful therapeutic outcome. “The approval of 9-δ-tetrahydocannabinol (THC)+
“The approval of 9-δ-tetrahydocannabinol (THC)+ “The consistency, efficacy, and safety of cannabis-based medicines have been demonstrated in humans, leading to the approval of the first cannabis-based therapy to alleviate spasticity and pain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Indeed, the evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of
“The consistency, efficacy, and safety of cannabis-based medicines have been demonstrated in humans, leading to the approval of the first cannabis-based therapy to alleviate spasticity and pain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Indeed, the evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of