 “The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies.
“The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies.
Cannabis sativa has long been known to contain antibacterial cannabinoids, but their potential to address antibiotic resistance has only been superficially investigated.
Here, we show that cannabinoids exhibit antibacterial activity against MRSA, inhibit its ability to form biofilms and eradicate pre-formed biofilms and stationary phase cells persistent to antibiotics.
We show that the mechanism of action of cannabigerol is through targeting the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive bacteria and demonstrate in vivo efficacy of cannabigerol in a murine systemic infection model caused by MRSA.
We also show that cannabinoids are effective against Gram-negative organisms whose outer membrane is permeabilized, where cannabigerol acts on the inner membrane.
Finally, we demonstrate that cannabinoids work in combination with polymyxin B against multi-drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens, revealing the broad-spectrum therapeutic potential for cannabinoids.”

 “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.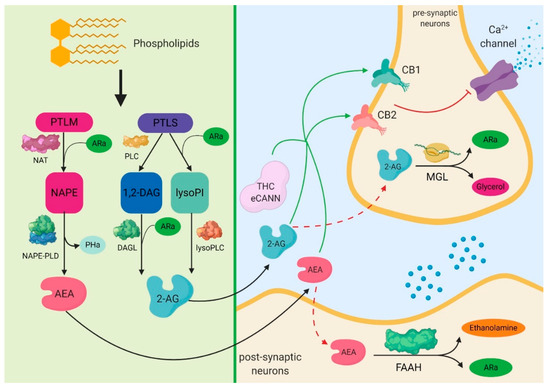
 “Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
“Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
 “Anticholinergic organophosphate (OP) agents act on the diverse serine hydrolases, thereby revealing unexpected biological effects. Epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between OP exposure and development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like symptoms, whereas no plausible mechanism for the OP-induced ADHD has been established.
“Anticholinergic organophosphate (OP) agents act on the diverse serine hydrolases, thereby revealing unexpected biological effects. Epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between OP exposure and development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like symptoms, whereas no plausible mechanism for the OP-induced ADHD has been established. “Activation of
“Activation of  “Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) and even induces remote organ damage.
“Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) and even induces remote organ damage. “Drugs selectively targeting CB2 hold promise for treating neurodegenerative disorders, inflammation, and pain while avoiding psychotropic side effects mediated by CB1. The mechanisms underlying CB2 activation and signaling are poorly understood but critical for drug design. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the human CB2-Gi signaling complex bound to the agonist WIN 55,212-2. The 3D structure reveals the binding mode of WIN 55,212-2 and structural determinants for distinguishing CB2 agonists from antagonists, which are supported by a pair of rationally designed agonist and antagonist. Further structural analyses with computational docking results uncover the differences between CB2 and CB1 in receptor activation, ligand recognition, and Gi coupling. These findings are expected to facilitate rational structure-based discovery of drugs targeting the
“Drugs selectively targeting CB2 hold promise for treating neurodegenerative disorders, inflammation, and pain while avoiding psychotropic side effects mediated by CB1. The mechanisms underlying CB2 activation and signaling are poorly understood but critical for drug design. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the human CB2-Gi signaling complex bound to the agonist WIN 55,212-2. The 3D structure reveals the binding mode of WIN 55,212-2 and structural determinants for distinguishing CB2 agonists from antagonists, which are supported by a pair of rationally designed agonist and antagonist. Further structural analyses with computational docking results uncover the differences between CB2 and CB1 in receptor activation, ligand recognition, and Gi coupling. These findings are expected to facilitate rational structure-based discovery of drugs targeting the  “The legalization of
“The legalization of  “This study aims to determine the frequency of coronary artery disease among young to middle aged adults presenting with chest pain who currently use marijuana as compared to nonusers.
“This study aims to determine the frequency of coronary artery disease among young to middle aged adults presenting with chest pain who currently use marijuana as compared to nonusers.