 “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
Both exogenous and endogenous CBs carry out a variety of physiological functions by engaging with two CB receptors, the CB1 and CB2 receptors, in the human endocannabinoid system (ECS). Both CB1 and CB2 are G protein-coupled receptors that share a 7-transmembrane (7TM) topology. CB1, known as the central CB receptor, is mainly distributed in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system. CB1 activation in the human body typically promotes the release of neurotransmitters, controls pain and memory learning, and regulates metabolism and the cardiovascular system.
Clinically, CB1 is a direct drug target for drug addiction, neurodegenerative diseases, pain, epilepsy, and obesity. Unlike the exclusive expression of CB1 in the nervous system, CB2 is mainly distributed in peripheral immune cells. Selective CB2 agonists would have therapeutic potential in the treatment of inflammation and pain and avoid side effects caused by currently used clinical drugs.
Although significant progress has been made in developing agonists toward CB receptors, efficient clinical drugs targeting CB receptors remain lacking due to their complex signaling mechanisms. The recent structural elucidation of CB receptors has greatly aided our understanding of the activation and signal transduction mechanisms of CB receptors.
Recent structural characterizations of CB receptors will greatly facilitate the design of new ligands to modulate the selective functions of CB receptors. Notably, the CBD was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 to treat epilepsy. We now look forward to more drugs targeting these two CB receptors for clinical usage in the near future.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32694501/
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-020-00240-5


 “Cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), as part of the endocannabinoid system, play a critical role in numerous human physiological and pathological conditions. Thus, considerable efforts have been made to develop ligands for CB1 and CB2, resulting in hundreds of phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids which have shown varying affinities relevant for the treatment of various diseases. However, only a few of these ligands are clinically used.
“Cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), as part of the endocannabinoid system, play a critical role in numerous human physiological and pathological conditions. Thus, considerable efforts have been made to develop ligands for CB1 and CB2, resulting in hundreds of phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids which have shown varying affinities relevant for the treatment of various diseases. However, only a few of these ligands are clinically used. “Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction.
“Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction. “Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use.
“Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use. “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.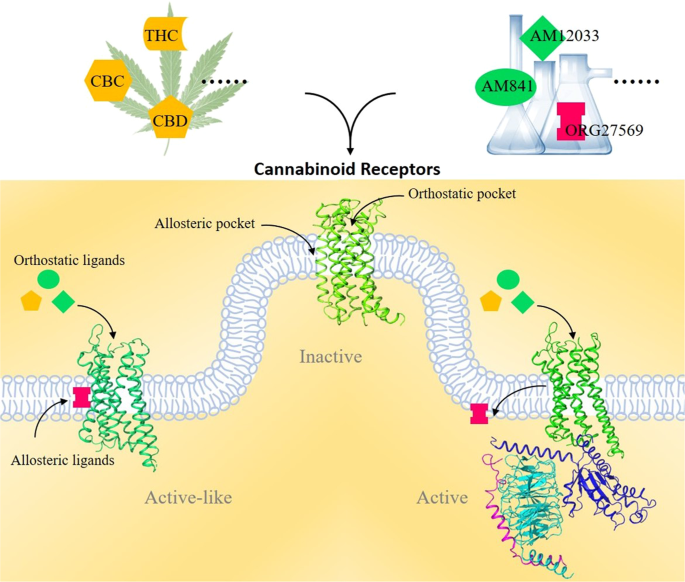
 “In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.”
“In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.” “During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions.
“During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions. “New neuroprotective treatments of natural origin are being investigated. Both, plant extracts and isolated compounds have shown bioactive effects.
“New neuroprotective treatments of natural origin are being investigated. Both, plant extracts and isolated compounds have shown bioactive effects.
 “Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
“Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”