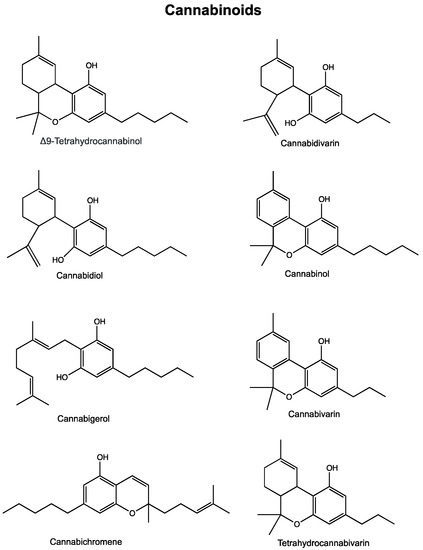
“Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye.
“Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye.
Recent findings: Allergic conjunctivitis and dry eye syndrome are common ocular surface diseases that have been treated with traditional pharmacological measures, e.g. corticosteroids, antihistamines. Given the side-effect profiles of these medications and the growing interest in complementary treatment modalities as part of integrative medical interventions, well known flavonoids, such as quercetin and catechin, are under investigation for topical and systemic application methods for relief. As flavonoid derivatives, pycnogenol and epigallocatechin gallate have alleviated dry eye symptoms, including lacrimal gland inflammation, tear secretion, and the stability of the tear film. Research on ocular cannabinoid receptors and response to synthetic cannabinoids are also being considered for therapy of anterior ocular disorders. The expansion of herbal formulations provides a framework for future treatment regimens for ocular surface disorders.
Summary: Flavonoids and cannabinoids show promise as potential complementary treatment for allergic diseases because of their anti-inflammatory and antiallergic properties. Several studies implementing ocular and systemic application of these compounds show potential in becoming adjuvant treatment strategies for improving quality of life while also managing ocular surface disease processes.”

 “Although several lines of evidence support the hypothesis of a dysregulation of serotoninergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), there is also evidence for an involvement of other pathways such as the GABAergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic systems.
“Although several lines of evidence support the hypothesis of a dysregulation of serotoninergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), there is also evidence for an involvement of other pathways such as the GABAergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic systems. “Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has proven to be an imminent threat to public health, intensifying the need for novel therapeutics.
“Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has proven to be an imminent threat to public health, intensifying the need for novel therapeutics. “Melanoma is the fourth most common type of cancer diagnosed in Australians after breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. While there has been substantial progress in the treatment of cancer in general, malignant melanoma, in particular, is resistant to existing medical therapies requiring an urgent need to develop effective treatments with lesser side effects.
“Melanoma is the fourth most common type of cancer diagnosed in Australians after breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. While there has been substantial progress in the treatment of cancer in general, malignant melanoma, in particular, is resistant to existing medical therapies requiring an urgent need to develop effective treatments with lesser side effects. “A significant number of epilepsy patients are refractory to conventional antiepileptic drugs. These patients experience considerable neurocognitive impairments that impact their quality of life and ability to function independently. This need for alternative treatment has generated increased interest in cannabis use as a therapeutic option in these patients.
“A significant number of epilepsy patients are refractory to conventional antiepileptic drugs. These patients experience considerable neurocognitive impairments that impact their quality of life and ability to function independently. This need for alternative treatment has generated increased interest in cannabis use as a therapeutic option in these patients.
 “Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction.
“Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction. “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.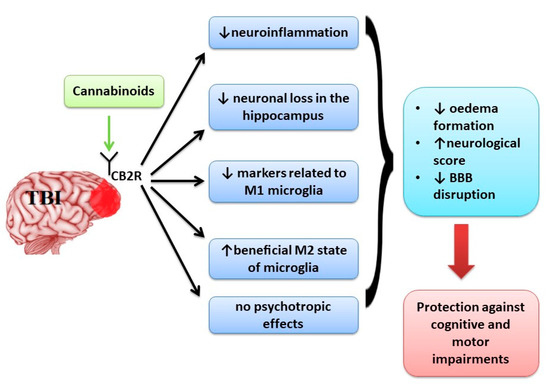
 “Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use.
“Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use. “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”