 “Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.
“Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) consists of a number of ligands, receptors and enzymes, and has gained interests in endometriosis research. This review aims to summarise all available evidence reporting the roles of the ECS in endometriosis.
A literature search of the PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science electronic medical databases was performed. Original and review articles published in peer-reviewed journals were included. No publication date or publication status restrictions were imposed.
Significant differences in the concentrations and expressions of the components of the ECS were reported in the eutopic and ectopic endometrium, and the systemic circulation of women with endometriosis compared to controls. Endometriosis appears to be associated with downregulation of CB1 receptors and upregulation of TRPV1 receptors.
The role of CB1 and progesterone in anti-inflammatory action and the role of TRPV1 in inflammation and pain are of particular interests. Furthermore, the ECS has been reported to be involved in processes relevant to endometriosis, including cell migration, cell proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, and interacts with sex steroid hormones.
The ECS may play a role in disease establishment, progression, and pain in endometriosis. However, reports are based on studies of limited size and there are inconsistencies among the definition of their control groups. There are also conflicting reports regarding precise involvement of the ECS in endometriosis. Future research with larger numbers, strict inclusion and exclusion criteria and detailed clinical information is imperative.”

 “Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances.
“Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances. “Available data support the notion that
“Available data support the notion that  “Endocannabinoid system consists of
“Endocannabinoid system consists of 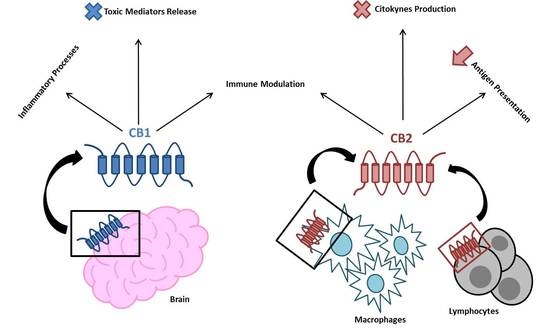
 “As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the
“As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the  “Excessive binge alcohol drinking may adversely affect cardiovascular function. In this study we characterize the detailed hemodynamic effects of an acute alcohol binge in mice using multiple approaches and investigate the role of the endocannabinoid-
“Excessive binge alcohol drinking may adversely affect cardiovascular function. In this study we characterize the detailed hemodynamic effects of an acute alcohol binge in mice using multiple approaches and investigate the role of the endocannabinoid-
 “Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the
“Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the 
 “Uncontrolled infection and increased inflammatory mediators might cause systemic inflammatory response. It is already known that
“Uncontrolled infection and increased inflammatory mediators might cause systemic inflammatory response. It is already known that  “Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder disorder with unclear etiology.
“Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder disorder with unclear etiology. “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.