 “The butyl homologues of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabutol (Δ9-THCB), and cannabidiol, cannabidibutol (CBDB), were isolated from a medicinal Cannabis sativa variety (FM2) inflorescence. Appropriate spectroscopic and spectrometric characterization, including NMR, UV, IR, ECD, and HRMS, was carried out on both cannabinoids. The chemical structures and absolute configurations of the isolated cannabinoids were confirmed by comparison with the spectroscopic data of the respective compounds obtained by stereoselective synthesis. The butyl homologue of Δ9-THC, Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (Ki = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (Ki = 51 nM) comparable to that of (-)-trans-Δ9-THC. Docking studies suggested the key bonds responsible for THC-like binding affinity for the CB1 receptor. The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor.”
“The butyl homologues of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabutol (Δ9-THCB), and cannabidiol, cannabidibutol (CBDB), were isolated from a medicinal Cannabis sativa variety (FM2) inflorescence. Appropriate spectroscopic and spectrometric characterization, including NMR, UV, IR, ECD, and HRMS, was carried out on both cannabinoids. The chemical structures and absolute configurations of the isolated cannabinoids were confirmed by comparison with the spectroscopic data of the respective compounds obtained by stereoselective synthesis. The butyl homologue of Δ9-THC, Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (Ki = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (Ki = 51 nM) comparable to that of (-)-trans-Δ9-THC. Docking studies suggested the key bonds responsible for THC-like binding affinity for the CB1 receptor. The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor.”
Category Archives: Uncategorized
A novel phytocannabinoid isolated from Cannabis sativa L. with an in vivo cannabimimetic activity higher than Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiphorol.

Medicinal and Synthetic Cannabinoids for Pediatric Patients: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet].
 “Cannabinoids are pharmacologically active agents extracted from the cannabis plant. Cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the most studied cannabinoids and both interact with endocannabinoid receptors in various human tissues. The endocannabinoid system moderates physiological functions, such as neurodevelopment, cognition, and motor control.
“Cannabinoids are pharmacologically active agents extracted from the cannabis plant. Cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the most studied cannabinoids and both interact with endocannabinoid receptors in various human tissues. The endocannabinoid system moderates physiological functions, such as neurodevelopment, cognition, and motor control.
The products naturally derived from cannabis include marijuana (dried leaves and flowers, mostly for smoking) and oral cannabinoid extracts with varying concentrations of cannabinoids, including cannabidiol and THC. THC is the main psychoactive constituent and cannabidiol seems to have no psychoactive properties. In addition, there are two synthetical cannabinoids approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, dronabinol and nabilone, which are molecules similar to a type of THC (δ-9-THC)1 Nabilone is also approved in Canada. Dronabinol is indicated for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children. The use of nabilone in children is not recommended.
In Canada, the minimum age for cannabis consumption varies by provinces and territories, and is either 18 or 19 years. A prescription is required to administer cannabinoids among children. Clinically, cannabis has been used to treat children with epilepsy, cancer palliation and primary treatment, chronic pain, and Parkinson disease.
The adverse events that clinicians need to monitor for include negative psychoactive sequelae and development of tolerance. Psychoactive sequelae may be positive, such as relaxation and euphoria, or negative, such as anxiety and irritability. In 2016, CADTH completed a Summary of Abstracts report on the use of cannabis in children with medical conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism spectrum disorder, Tourette syndrome, epilepsy, posttraumatic stress disorder, or neurodegenerative diseases, and five non-randomized studies were identified. However, there were no control groups in the five studies included in the report.
It is unclear whether there is new evidence or clinical guidance for the use of medical cannabis in children with mental health conditions, neurodegenerative diseases, or pain disorders, particularly in comparison with other possible therapies for those conditions. There is a need to review the clinical effectiveness of cannabis for pediatric care, as well as clinical guidelines.”
Pharmacists and the future of cannabis medicine.
 “To summarize the history and evolution of cannabis use and policies and to review current therapeutic uses, safety, and the central role pharmacists can play.
“To summarize the history and evolution of cannabis use and policies and to review current therapeutic uses, safety, and the central role pharmacists can play.
SUMMARY:
Cannabis regulation and use have evolved over the centuries and are becoming more widely accepted, with over two-thirds of states in the United States having an approved cannabis program. However, changing policy and a paucity of controlled clinical trials has led to questions on the safety and effectiveness of cannabinoid therapies. Although there are conditions for which cannabinoids may be helpful, potential contraindications, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions should be taken into account.
CONCLUSION:
Pharmacists are in a unique position based on their accessibility, knowledge, and skills to guide product selection, dosing, and discuss drug interactions and adverse effects to educate patients on safe cannabis use, whether it be delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, or a combination thereof. Pharmacists and pharmacy organizations, moreover, should advocate for an integral role in the medical cannabis movement to ensure patient safety and evaluate cannabinoid pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, drug-drug interactions, safety, and efficacy through rigorous investigations.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31870860
https://www.japha.org/article/S1544-3191(19)30513-8/fulltext
Cannabis and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: An Updated Review.
“Cannabis plant has the scientific name called Cannabis sativa L. Cannabis plant has many species, but there are three main species including Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica and Cannabis ruderalis. Over 70 compounds isolated from cannabis species are called cannabinoids (CBN).
Cannabinoids produce over 100 naturally occurring chemicals. The most abundant chemicals are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD). THC is psychotropic chemical that makes people feel “high” while CBD is nonpsychotropic chemical. However, cannabinoid chemicals are not found only in the cannabis plant, they are also produced by the mammalian body, called endocannabinoids and in the laboratory, called synthesized cannabinoids.
Endocannabinoids are endogenous lipid-based retrograde neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the mammalian central nervous system including brain and peripheral nervous system. There are at least two types of endocannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) which are G-protein coupled receptors.
CB1 receptors are particularly abundant in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, hypothalamus and cerebellum, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. They are present in inhibitory GABA-ergic neurons and excitatory glutamatergic neurons. CB2 receptor is most abundantly found on cells of the immune system, hematopoietic cells and glia cells. CB2 is mainly expressed in the periphery under normal healthy condition, but in conditions of disease or injury, this upregulation occurs within the brain, and CB2 is therefore expressed in the brain in unhealthy states.
Cannabis and cannabinoid are studied in different medical conditions. The therapeutic potentials of both cannabis and cannabinoid are related to the effects of THC, CBD and other cannabinoid compounds. However, the “high” effect of THC in cannabis and cannabinoid may limit the clinical use, particularly, the study on the therapeutic potential of THC alone is more limited.
This review emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD and CBD with THC. CBD has shown to have benefit in a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders including autism spectrum disorder, anxiety, psychosis, neuropathic pain, cancer pain, HIV, migraine, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, Huntington disease, hypoxic-ischemic injury and epilepsy. CBD is generally well tolerated. Most common adverse events are diarrhea and somnolence. CBD also shows significantly low abuse potential.”
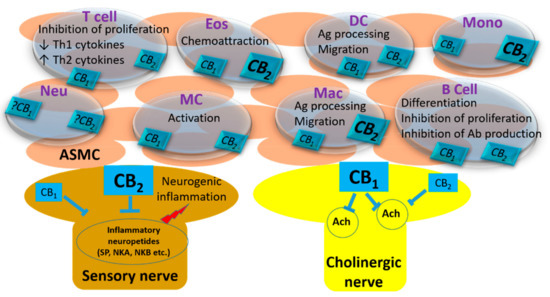
Endocannabinoid System in the Airways.
 “Cannabinoids and the mammalian endocannabinoid system is an important research area of interest and attracted many researchers because of their widespread biological effects. The significant immune-modulatory role of cannabinoids has suggested their therapeutic use in several inflammatory conditions. Airways are prone to environmental irritants and stimulants, and increased inflammation is an important process in most of the respiratory diseases. Therefore, the main strategies for treating airway diseases are suppression of inflammation and producing bronchodilation. The ability of cannabinoids to induce bronchodilation and modify inflammation indicates their importance for airway physiology and pathologies. In this review, the contribution of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in the airways are discussed, and the existing data for their therapeutic use in airway diseases are presented.”
“Cannabinoids and the mammalian endocannabinoid system is an important research area of interest and attracted many researchers because of their widespread biological effects. The significant immune-modulatory role of cannabinoids has suggested their therapeutic use in several inflammatory conditions. Airways are prone to environmental irritants and stimulants, and increased inflammation is an important process in most of the respiratory diseases. Therefore, the main strategies for treating airway diseases are suppression of inflammation and producing bronchodilation. The ability of cannabinoids to induce bronchodilation and modify inflammation indicates their importance for airway physiology and pathologies. In this review, the contribution of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in the airways are discussed, and the existing data for their therapeutic use in airway diseases are presented.”
Stress-induced modulation of endocannabinoid signaling leads to delayed strengthening of synaptic connectivity in the amygdala.
 “Even a brief exposure to severe stress strengthens synaptic connectivity days later in the amygdala, a brain area implicated in the affective symptoms of stress-related psychiatric disorders. However, little is known about the synaptic signaling mechanisms during stress that eventually culminate in its delayed impact on the amygdala. Hence, we investigated early stress-induced changes in amygdalar synaptic signaling in order to prevent its delayed effects.
“Even a brief exposure to severe stress strengthens synaptic connectivity days later in the amygdala, a brain area implicated in the affective symptoms of stress-related psychiatric disorders. However, little is known about the synaptic signaling mechanisms during stress that eventually culminate in its delayed impact on the amygdala. Hence, we investigated early stress-induced changes in amygdalar synaptic signaling in order to prevent its delayed effects.
Whole-cell recordings in basolateral amygdala (BLA) slices from rats revealed higher frequency of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) immediately after 2-h immobilization stress. This was replicated by inhibition of cannabinoid receptors (CB1R), suggesting a role for endocannabinoid (eCB) signaling.
Stress also reduced N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA), an endogenous ligand of CB1R. Since stress-induced activation of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) reduces AEA, we confirmed that oral administration of an FAAH inhibitor during stress prevents the increase in synaptic excitation in the BLA soon after stress.
Although stress also caused an immediate reduction in synaptic inhibition, this was not prevented by FAAH inhibition. Strikingly, FAAH inhibition during the traumatic stressor was also effective 10 d later on the delayed manifestation of synaptic strengthening in BLA neurons, preventing both enhanced mEPSC frequency and increased dendritic spine-density.
Thus, oral administration of an FAAH inhibitor during a brief stress prevents the early synaptic changes that eventually build up to hyperexcitability in the amygdala. This framework is of therapeutic relevance because of growing interest in targeting eCB signaling to prevent the gradual development of emotional symptoms and underlying amygdalar dysfunction triggered by traumatic stress.”
Cannabinoids and dystonia: an issue yet to be defined.
 “Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained or intermittent muscle contractions causing abnormal movements and postures. Besides motor manifestations, patients with dystonia also display non-motor signs and symptoms including psychiatric and sensory disturbances.
“Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained or intermittent muscle contractions causing abnormal movements and postures. Besides motor manifestations, patients with dystonia also display non-motor signs and symptoms including psychiatric and sensory disturbances.
Symptomatic treatment of motor signs in dystonia largely relies on intramuscular botulinum toxin injections and, in selected cases, on deep brain stimulation. Oral medications and physical therapy offer a few benefits only in a minority of patients.
Cannabinoids have been shown to be a complementary treatment in several neurological disorders but their usefulness in dystonia have not been systematically assessed. Given recent policy changes in favor of cannabis use in clinical practice and the request for alternative treatments, it is important to understand how cannabinoids may impact people with dystonia.
Reviewing the evidence so far available and our own experience, cannabinoids seem to be effective in single cases but further studies are required to improve our understanding on their role as complementary treatment in dystonia.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31848779
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10072-019-04196-5
Beta-caryophyllene enhances wound healing through multiple routes.
 “Beta-caryophyllene is an odoriferous bicyclic sesquiterpene found in various herbs and spices.
“Beta-caryophyllene is an odoriferous bicyclic sesquiterpene found in various herbs and spices.
Recently, it was found that beta-caryophyllene is a ligand of the cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Activation of CB2 will decrease pain, a major signal for inflammatory responses.
We hypothesized that beta-caryophyllene can affect wound healing by decreasing inflammation. Here we show that cutaneous wounds of mice treated with beta-caryophyllene had enhanced re-epithelialization.
The treated tissue showed increased cell proliferation and cells treated with beta-caryophyllene showed enhanced cell migration, suggesting that the higher re-epithelialization is due to enhanced cell proliferation and cell migration. The treated tissues also had up-regulated gene expression for hair follicle bulge stem cells. Olfactory receptors were not involved in the enhanced wound healing. Transient Receptor Potential channel genes were up-regulated in the injured skin exposed to beta-caryophyllene. Interestingly, there were sex differences in the impact of beta- caryophyllene as only the injured skin of female mice had enhanced re-epithelialization after exposure to beta-caryophyllene.
Our study suggests that chemical compounds included in essential oils have the capability to improve wound healing, an effect generated by synergetic impacts of multiple pathways.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31841509
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0216104
“β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a common constitute of the essential oils of numerous spice, food plants and major component in Cannabis.” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23138934
“Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18574142
Medicinal Use of Cannabis in Children and Pregnant Women.
 “The increasing medicinal use of cannabis during recent years has largely overlooked children and pregnant women due to litigious and ethical concerns.
“The increasing medicinal use of cannabis during recent years has largely overlooked children and pregnant women due to litigious and ethical concerns.
However, over the last few years medicine has observed increasing numbers of children treated with cannabis for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), and pregnant women treated for hyperemesis gravidarum (HG).
This review provides an account of major findings discovered through this research.
Specifically, cannabis may offer therapeutic advantages to behavioral symptoms of autism spectrum disorder and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, and to the severe nausea and vomiting in hyperemesis gravidarum.
The use of medical cannabis in children and pregnant women should be further discussed and researched in this patient population.”
