 “Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by aberrant bone marrow plasma cell (PC) proliferation and is one of the most common hematological malignancies. The potential effect of cannabinoids on the immune system and hematological malignancies has been poorly characterized.
“Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by aberrant bone marrow plasma cell (PC) proliferation and is one of the most common hematological malignancies. The potential effect of cannabinoids on the immune system and hematological malignancies has been poorly characterized.
Cannabidiol (CBD) may be used to treat various diseases. CBD is known to exert immunomodulatory effects through the activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), which is expressed in high levels in the hematopoietic system.
Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells are a heterogeneous population of polyclonal T lymphocytes obtained via ex vivo sequential incubation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with interferon-γ (IFN-γ), anti CD3 monoclonal antibody, and IL-2. They are characterized by the expression of CD3+ and CD56+, which are surface markers common to T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. CIK cells are mainly used in hematological patients who suffer relapse after allogeneic transplantation.
Here, we investigated their antitumor effect in combination with pure cannabidiol in KMS-12 MM cells by lactate dehydrogenase LDH cytotoxicity assay, CCK-8 assay, and flow cytometry analysis. The surface and intracellular CB2 expressions on CIK cells and on KMS-12 and U-266 MM cell lines were also detected by flow cytometry.
Our findings confirm that the CB2 receptor is highly expressed on CIK cells as well as on MM cells. CBD was able to decrease the viability of tumor cells and can have a protective role for CIK cells. It also inhibits the cytotoxic activity of CIKs against MM at high concentrations, so in view of a clinical perspective, it has to be considered that the lower concentration of 1 µM can be used in combination with CIK cells. Further studies will be required to address the mechanism of CBD modulation of CIK cells in more detail.”

 “Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.
“Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.
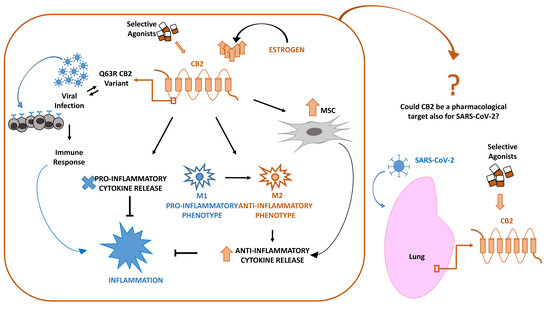

 “Cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) is a complex, polymorphic plant species, which produces a vast array of bioactive metabolites, the two major chemical groups being cannabinoids and terpenoids. Nonetheless, the psychoactive cannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ 9 -THC) and the non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD), are the two major cannabinoids that have monopolized the research interest.
“Cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) is a complex, polymorphic plant species, which produces a vast array of bioactive metabolites, the two major chemical groups being cannabinoids and terpenoids. Nonetheless, the psychoactive cannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ 9 -THC) and the non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD), are the two major cannabinoids that have monopolized the research interest.
 “Four pivotal randomized placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated that adjunctive therapy with cannabidiol (CBD) improves seizure control in patients with Dravet syndrome (DS) and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS).
“Four pivotal randomized placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated that adjunctive therapy with cannabidiol (CBD) improves seizure control in patients with Dravet syndrome (DS) and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS). “The market for products featuring hemp extracts is large and growing larger. However, safety concerns have been raised by medical and regulatory agencies. Post marketing surveillance of full spectrum hemp extract (FSHE) products manufactured and distributed by CV Sciences (CVSI) and traded under the brand PlusCBD™ was conducted over a 2-year period (2018-2019). The safety of these products was assessed by analyzing adverse events reports.
“The market for products featuring hemp extracts is large and growing larger. However, safety concerns have been raised by medical and regulatory agencies. Post marketing surveillance of full spectrum hemp extract (FSHE) products manufactured and distributed by CV Sciences (CVSI) and traded under the brand PlusCBD™ was conducted over a 2-year period (2018-2019). The safety of these products was assessed by analyzing adverse events reports. “Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.
“Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, affecting ambulation even in people with only mild neurological signs. Patients with MS frequently experience spasticity, which contributes significantly to impair their motor functions, including ambulation, owing to muscle stiffness, spasms, and pain.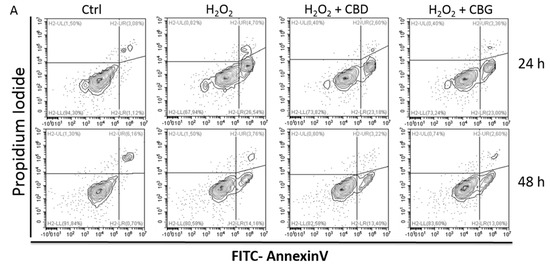
 “In the last years, clinical and preclinical researchers have increased their interest in non-psychotomimetic cannabinoids, like cannabidiol (CBD), as a strategy for treating psychostimulant use disorders. However, there are discrepancies in the pharmacological effects and brain targets of CBD.
“In the last years, clinical and preclinical researchers have increased their interest in non-psychotomimetic cannabinoids, like cannabidiol (CBD), as a strategy for treating psychostimulant use disorders. However, there are discrepancies in the pharmacological effects and brain targets of CBD.