“Positive effect of some cannabinoids in the treatment and prophylaxis of a wide variety of oxidation-associated diseases and growing popularity of supplements containing cannabinoids, mainly cannabinoid oils (e.g. CBD oil, CBG oil), in the self-medication of humans cause a growing interest in the antioxidant properties of these compounds, especially those not showing psychotropic effects.
“Positive effect of some cannabinoids in the treatment and prophylaxis of a wide variety of oxidation-associated diseases and growing popularity of supplements containing cannabinoids, mainly cannabinoid oils (e.g. CBD oil, CBG oil), in the self-medication of humans cause a growing interest in the antioxidant properties of these compounds, especially those not showing psychotropic effects.
Herein, we report the antioxidant activity of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiol (CBD), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabinolic acid (CBDA) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (Δ9-THCA) estimated by spectrophotometric methods: ABTS, DPPH, ORAC, beta-carotene CUPRAC and FRAP.
The presented data prove that all the examined cannabinoids exhibit antioxidant activity manifested in their ability to scavenge free radicals, to prevent the oxidation process and to reduce metal ions. Although the intensity of these activities is not the same for the individual cannabinoids it is comparable for all of them with that of E vitamin.”
“The present paper discusses the antioxidant properties of CBG, CBN, CBDA, CBGA and Δ9-THCA which, beside CBD and Δ9-THC, are also supposed to be bioactive compounds useful in the therapeutic treatment of different diseases. According to the literature, CBD and Δ9-THC exhibit strong antioxidant activity, stronger than vitamins C, A and E.
The presented data prove that all the examined cannabinoids – CBG, CBD, Δ9-THC, CBN, CBGA CBDA and Δ9-THCA – exhibit antioxidant activity manifesting itself in their ability to scavenge free radicals, to protect oxidation process and to reduce metal ions. Although, the intensity of these activities for individual cannabinoids is not the same, it is generally comparable to that of E vitamin.” https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0367326X21000903?via%3Dihub

 “Streptococcus mutans
“Streptococcus mutans “The relevance and incidence of intestinal bowel diseases (IBD) have been increasing over the last 50 years and the current therapies are characterized by severe side effects, making essential the development of new strategies that combine efficacy and safety in the management of human IBD. Herbal products are highly considered in research aimed at discovering new approaches for IBD therapy and, among others,
“The relevance and incidence of intestinal bowel diseases (IBD) have been increasing over the last 50 years and the current therapies are characterized by severe side effects, making essential the development of new strategies that combine efficacy and safety in the management of human IBD. Herbal products are highly considered in research aimed at discovering new approaches for IBD therapy and, among others,  “Preclinical studies have shown cannabidiol is protective in models of ischemic stroke. Based on results from our recent systematic review, we investigated the effects of two promising neuroprotective phytocannabinoids, cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabidivarin (CBDV), on cells of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), namely human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs), pericytes, and astrocytes.
“Preclinical studies have shown cannabidiol is protective in models of ischemic stroke. Based on results from our recent systematic review, we investigated the effects of two promising neuroprotective phytocannabinoids, cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabidivarin (CBDV), on cells of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), namely human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs), pericytes, and astrocytes. “An observational research design was used to evaluate which types of commonly labeled Cannabis flower product characteristics are associated with changes in momentary feelings of distress-related symptoms.
“An observational research design was used to evaluate which types of commonly labeled Cannabis flower product characteristics are associated with changes in momentary feelings of distress-related symptoms. “Foodborne protein hydrolysates exhibit biological activity that may be therapeutic in a number of human disease settings. Hemp peptides (HP) generated by controlled hydrolysis of hemp proteins have a number of health benefits and are of pharmaceutical value. In the present study, we produce small molecular weight HP from hemp seed and investigate its anticancer properties in Hep3B human liver cancer cells. We demonstrate that HP treatment increased apoptosis, reduced cell viability, and reduced cell migration in Hep3B human liver cancer cells without affecting the normal liver cell line L02. We correlate these phenotypes with increased cellular ROS levels, upregulation of cleaved caspase 3 and Bad, and downregulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2. HP treatment led to increased Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation, with subsequent downregulation of β-catenin, suggesting β-catenin signaling modulation as a critical mechanism by which HP exhibits anticancer properties. Our findings suggest HP are of potential therapeutic interest for liver cancer treatment.”
“Foodborne protein hydrolysates exhibit biological activity that may be therapeutic in a number of human disease settings. Hemp peptides (HP) generated by controlled hydrolysis of hemp proteins have a number of health benefits and are of pharmaceutical value. In the present study, we produce small molecular weight HP from hemp seed and investigate its anticancer properties in Hep3B human liver cancer cells. We demonstrate that HP treatment increased apoptosis, reduced cell viability, and reduced cell migration in Hep3B human liver cancer cells without affecting the normal liver cell line L02. We correlate these phenotypes with increased cellular ROS levels, upregulation of cleaved caspase 3 and Bad, and downregulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2. HP treatment led to increased Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation, with subsequent downregulation of β-catenin, suggesting β-catenin signaling modulation as a critical mechanism by which HP exhibits anticancer properties. Our findings suggest HP are of potential therapeutic interest for liver cancer treatment.” “Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”
“Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”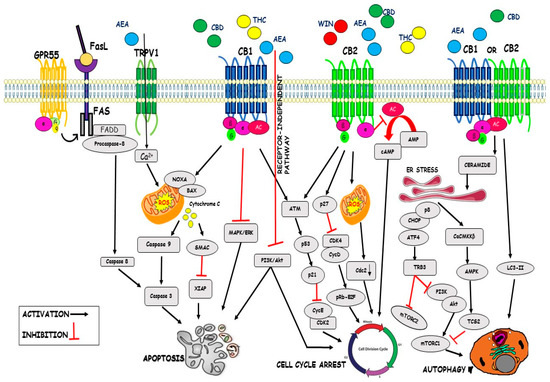
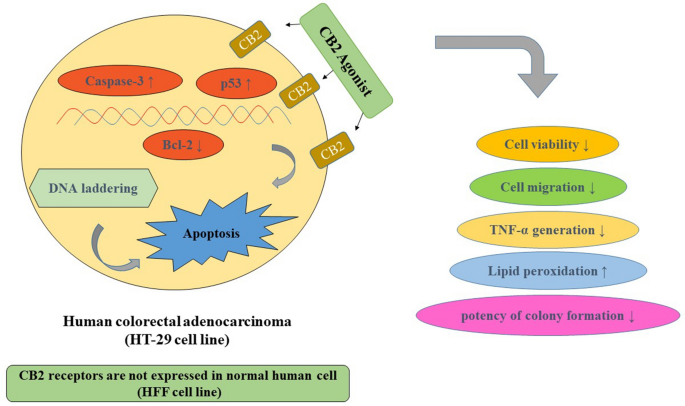
 “Colorectal cancer (CRC) is between the top three occurring cancers worldwide. The anticancer effects of Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB
“Colorectal cancer (CRC) is between the top three occurring cancers worldwide. The anticancer effects of Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB