 “Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
“Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
Cardiotoxicity induced by anti-cancer treatments compromise vasospastic and thromboembolic ischemia, dysrhythmia, hypertension, myocarditis, and cardiac dysfunction that can result in heart failure. Importantly, none of the strategies to prevent cardiotoxicity from anticancer therapies is completely safe and satisfactory.
Certain clinically used cardioprotective drugs can even contribute to cancer induction. Since G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are target of forty percent of clinically used drugs, here we discuss the newly identified cardioprotective agents that bind GPCRs of adrenalin, adenosine, melatonin, ghrelin, galanin, apelin, prokineticin and cannabidiol.
We hope to provoke further drug development studies considering these GPCRs as potential targets to be translated to treatment of human heart failure induced by anticancer drugs.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32039239
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2019.00194/full

 “Dravet syndrome (DS) is one of the most severe forms of drug-resistant epilepsy and available interventions fail to control seizures in most patients.
“Dravet syndrome (DS) is one of the most severe forms of drug-resistant epilepsy and available interventions fail to control seizures in most patients. “The rationale of this study was to assess occurrence of withdrawal symptoms induced by abrupt cessation of cannabidiol (CBD) after prolonged administration in healthy volunteers.
“The rationale of this study was to assess occurrence of withdrawal symptoms induced by abrupt cessation of cannabidiol (CBD) after prolonged administration in healthy volunteers. “Neuropsychiatric disorders, such as addiction, are associated with cognitive impairment, including learning and memory deficits.
“Neuropsychiatric disorders, such as addiction, are associated with cognitive impairment, including learning and memory deficits. “The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing.
“The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing. “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.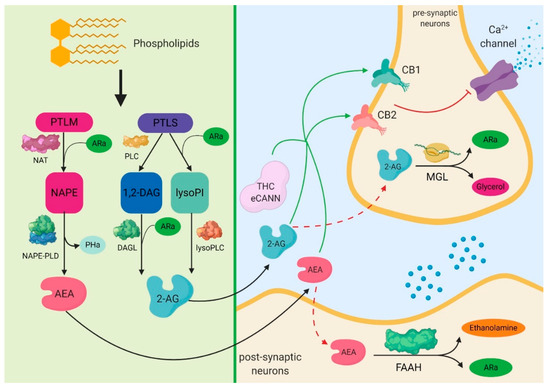
 “Recent evidence suggests that
“Recent evidence suggests that  “Palliative medicine physicians are challenged by lack of guidance regarding effectiveness and dosing of cannabis products in the setting of their emerging popularity.
“Palliative medicine physicians are challenged by lack of guidance regarding effectiveness and dosing of cannabis products in the setting of their emerging popularity. “Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain.
“Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain.