 “Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.”
“Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33562819/
“Among primary brain tumours, glioblastoma is the most aggressive. As early relapses are unavoidable despite standard-of-care treatment, the cannabinoids delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) alone or in combination have been suggested as a combined treatment strategy for glioblastomas. However, the known psychoactive effects of THC hamper its medical applications in these patients with potential cognitive impairment due to the progression of the disease. Therefore, nontoxic cannabigerol (CBG), being recently shown to exhibit anti-tumour properties in some carcinomas, is assayed here for the first time in glioblastoma with the aim to replace THC. We indeed found CBG to effectively impair the relevant hallmarks of glioblastoma progression, with comparable killing effects to THC and in addition inhibiting the invasion of glioblastoma cells. Moreover, CBG can destroy therapy-resistant glioblastoma stem cells, which are the root of cancer development and extremely resistant to various other treatments of this lethal cancer. CBG should present a new yet unexplored adjuvant treatment strategy of glioblastoma.”

 “Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant)
“Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant) 


 “Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals that bind to receptors in the human body and, in turn, modulate the endocannabinoid system (ECS). They can be endogenously produced, synthetic, or derived from the plant Cannabis sativa L.
“Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals that bind to receptors in the human body and, in turn, modulate the endocannabinoid system (ECS). They can be endogenously produced, synthetic, or derived from the plant Cannabis sativa L.
 “Derivatives of the plant Cannabis sativa have been used for centuries for both medical and recreational purposes, as well as industrial. The first proof of its medicinal use comes from ancient China, although there is evidence of its earlier utilization in Europe and Asia. In the 19th century, European practitioners started to employ cannabis extracts to treat tetanus, convulsions, and mental diseases and, in 1851, cannabis made its appearance in the Pharmacopoeia of the United States as an analgesic, hypnotic and anticonvulsant. It was only in 1937 that the Marijuana Tax Act prohibited the use of this drug in the USA. The general term Cannabis is commonly used by the scientific and scholar community to indicate derivatives of the plant Cannabis sativa. The word cannabinoid is a term describing chemical compounds that are either derivate of Cannabis (phytocannabinoids) or artificial analogues (synthetic) or are produced endogenously by the body (endocannabinoids). A more casual term “marijuana” or “weed”, a compound derived from dried Cannabis flower tops and leaves, has progressively superseded the term cannabis when referred to its recreational use. The 2018 World health organisation (WHO) data suggest that nearly 2.5% of the global population (147 million) uses marijuana and some countries, such as Canada and Uruguay, have already legalised it. Due to its controversial history, the medicinal use of cannabinoids has always been a centre of debate. The isolation and characterisation of Δ9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the major psychoactive component of cannabis and the detection of two human cannabinoid receptor (CBRs) molecules renewed interest in the medical use of cannabinoids, boosting research and commercial heed in this sector. Some cannabinoid-based drugs have been approved as medications, mainly as antiemetic, antianorexic, anti-seizure remedies and in cancer and multiple sclerosis patients’ palliative care. Nevertheless, due to the stigma commonly associated with these compounds, cannabinoids’ potential in the treatment of conditions such as cancer is still largely unknown and therefore underestimated.”
“Derivatives of the plant Cannabis sativa have been used for centuries for both medical and recreational purposes, as well as industrial. The first proof of its medicinal use comes from ancient China, although there is evidence of its earlier utilization in Europe and Asia. In the 19th century, European practitioners started to employ cannabis extracts to treat tetanus, convulsions, and mental diseases and, in 1851, cannabis made its appearance in the Pharmacopoeia of the United States as an analgesic, hypnotic and anticonvulsant. It was only in 1937 that the Marijuana Tax Act prohibited the use of this drug in the USA. The general term Cannabis is commonly used by the scientific and scholar community to indicate derivatives of the plant Cannabis sativa. The word cannabinoid is a term describing chemical compounds that are either derivate of Cannabis (phytocannabinoids) or artificial analogues (synthetic) or are produced endogenously by the body (endocannabinoids). A more casual term “marijuana” or “weed”, a compound derived from dried Cannabis flower tops and leaves, has progressively superseded the term cannabis when referred to its recreational use. The 2018 World health organisation (WHO) data suggest that nearly 2.5% of the global population (147 million) uses marijuana and some countries, such as Canada and Uruguay, have already legalised it. Due to its controversial history, the medicinal use of cannabinoids has always been a centre of debate. The isolation and characterisation of Δ9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the major psychoactive component of cannabis and the detection of two human cannabinoid receptor (CBRs) molecules renewed interest in the medical use of cannabinoids, boosting research and commercial heed in this sector. Some cannabinoid-based drugs have been approved as medications, mainly as antiemetic, antianorexic, anti-seizure remedies and in cancer and multiple sclerosis patients’ palliative care. Nevertheless, due to the stigma commonly associated with these compounds, cannabinoids’ potential in the treatment of conditions such as cancer is still largely unknown and therefore underestimated.” “Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.
“Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.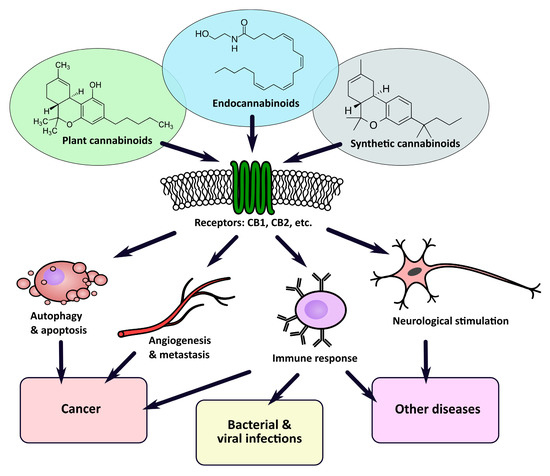
 “Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.
“Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.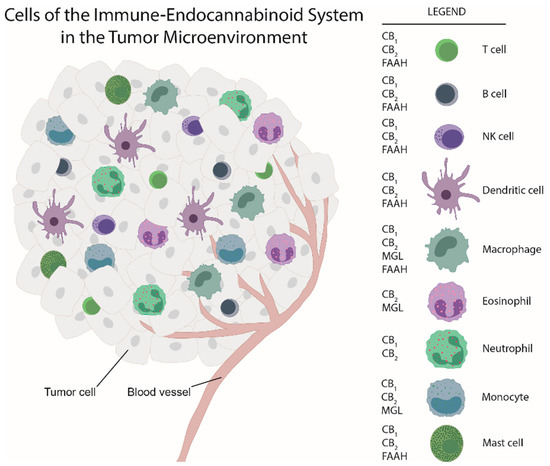
 “Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy.
“Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy. “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.