“A special component of cannabis, cannabidiol (CBD), is currently in the focus of epilepsy treatment and research. In this context, we investigated patients’ expectations and preferences pertaining to plant-derived versus synthetic formulation of cannabidiol, as well as their willingness to get this treatment.
Methods: One hundred and four of 153 patients with different forms of epilepsy (54 % female, mean age 40 ± 16 yrs.) responded to the survey. The survey consisted of 8 questions addressing expectations of and concerns towards CBD treatment, preferences of plant-derived versus synthetic CBD, estimated monthly costs, and willingness to buy CBD at one’s own expense.
Results: The majority (73 %) of the responding epilepsy patients wished to receive plant-derived CBD; 5 % preferred synthetic CBD. Reasons for this choice were botanic origin, lack of chemistry, and the assumption of fewer and less dangerous side effects. Eighty-two percent of the patients estimated the monthly costs of CBD treatment to be below €500. Using the willingness-to-pay approach to assess the commitment of patients, 68 % could imagine buying the drug themselves. Fifty-three percent of these would be willing to pay up to €100, 40 % €100 to €200, and another 7 % €200 to €500 per month.
Conclusion: There is an overwhelming preference towards plant-derived cannabidiol in epilepsy patients, driven by the idea of organic substances being safer and better tolerated than synthetic. The willingness-to-pay approach reflects the high burden and pressure of uncontrolled epilepsy and the expectation of relief. Non-realistic ideas of pricing as well as what patients would be willing and able to pay confirm this perception.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32554292/
“Epilepsy patients preferred plant-derived cannabidiol to synthetic cannabidiol.”
https://www.seizure-journal.com/article/S1059-1311(20)30175-8/pdf

 “Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets.
“Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets. “Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated.
“Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated. “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.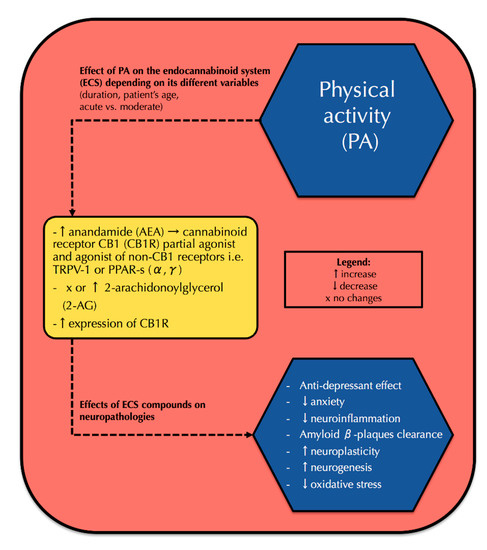
 “The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.
“The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.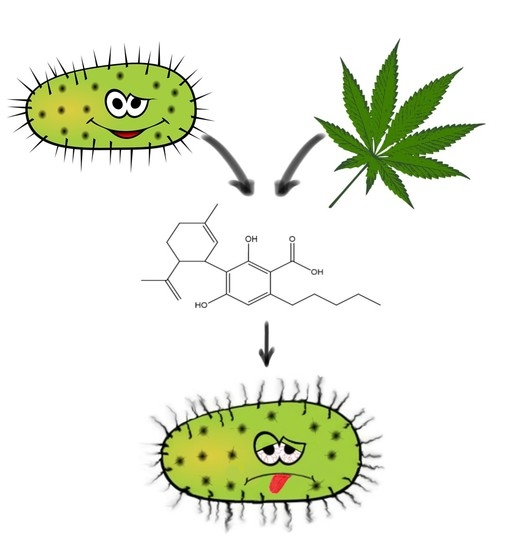
 “Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology.
“Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology. ‘T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a highly heterogeneous malignant hematological disorder arising from T-cell progenitors.
‘T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a highly heterogeneous malignant hematological disorder arising from T-cell progenitors. “Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization.
“Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization. “Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency.
“Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency.