 “Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
“Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
Methods: Semistructured telephone interviews were conducted in a convenience sample of individuals (n = 24) with physician-confirmed oncologic diagnoses and state/district authorization to use MC (Arizona, California, Florida, Illinois, Massachusetts, Oregon, New York, and Washington, DC) from April 2017 to March 2019. Standard qualitative techniques were used to assess the degree of MC-related health care oversight, MC practices, and key information sources.
Results: Among 24 participants (median age, 57 years; range, 30-71 years; 16 women [67%]), MC certifications were typically issued by a professional new to a patient’s care after a brief, perfunctory consultation. Patients disclosed MCuse to their established medical teams but received little medical advice about whether and how to use MC. Patients with cancer used MC products as multipurpose symptom management and as cancer-directed therapy, sometimes in lieu of standard-of-care treatments. Personal experimentation, including methodical self-monitoring, was an important source of MC know-how. Absent formal advice from medical professionals, patients relied on nonmedical sources for MC information.
Conclusions: Patients with cancer used MC with minimal medical oversight. Most received MC certifications through brief meetings with unfamiliar professionals. Participants desired but were often unable to access high-quality clinical information about MC from their established medical teams. Because many patients are committed to using MC, a product sustained by a growing industry, medical providers should familiarize themselves with the existing data for MM and its limitations to address a poorly met clinical need.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32986266/
“Notably, oncology patients reported using medical cannabis (MC) for symptom management and as cancer‐directed therapy, sometimes instead of traditional treatments.”
https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.33202

 “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”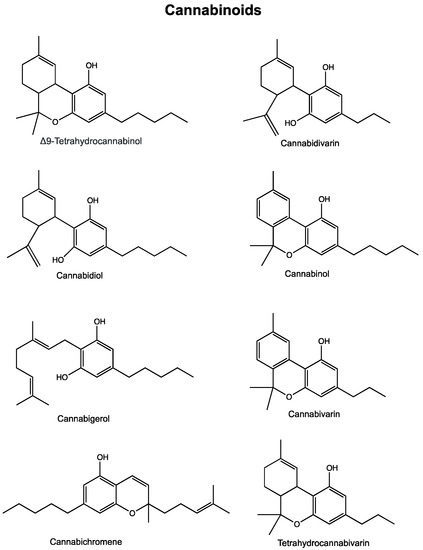
 “In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
“In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
 “The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.
“The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.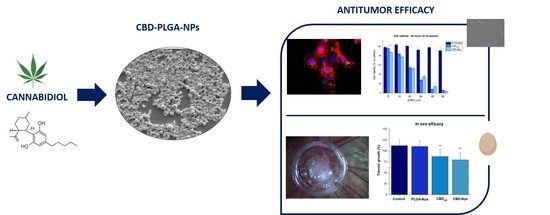
 “The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.
“The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.  “In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions.
“In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions. “Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) affect the human endocannabinoid system.
“Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) affect the human endocannabinoid system. “To evaluate interest in and patterns of use of non-prescription
“To evaluate interest in and patterns of use of non-prescription  “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a multifunctional homeostatic system involved in many physiological and pathological conditions. The ligands of the ECS are the endocannabinoids, whose actions are mimicked by exogenous cannabinoids, such as phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids. Responses to the ligands of the ECS are mediated by numerous receptors like the classical cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) as well as ECS-related receptors, e.g., G protein-coupled receptors 18 and 55 (GPR18 and GPR55), transient receptor potential ion channels, and nuclear peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. The ECS regulates almost all levels of female reproduction, starting with oocyte production through to parturition. Dysregulation of the ECS is associated with the development of gynecological disorders from fertility disorders to cancer. Cannabinoids that act at the ECS as specific agonists or antagonists may potentially influence dysregulation and, therefore, represent new therapeutic options for the therapy of gynecological disorders.”
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a multifunctional homeostatic system involved in many physiological and pathological conditions. The ligands of the ECS are the endocannabinoids, whose actions are mimicked by exogenous cannabinoids, such as phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids. Responses to the ligands of the ECS are mediated by numerous receptors like the classical cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) as well as ECS-related receptors, e.g., G protein-coupled receptors 18 and 55 (GPR18 and GPR55), transient receptor potential ion channels, and nuclear peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. The ECS regulates almost all levels of female reproduction, starting with oocyte production through to parturition. Dysregulation of the ECS is associated with the development of gynecological disorders from fertility disorders to cancer. Cannabinoids that act at the ECS as specific agonists or antagonists may potentially influence dysregulation and, therefore, represent new therapeutic options for the therapy of gynecological disorders.” “Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment.
“Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment.