 “To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.
“To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.
Results: There were no between-group differences based on demographic, experiential, or attitudinal variables. We found that 50.8% were able to stop all opioid usage, which took a median of 6.4 years (IQR=1.75-11 years) after excluding two patients who transitioned off opioids by utilizing opioid agonists. For those 29 patients (47.5%) who did not stop opioids, 9 (31%) were able to reduce opioid use, 3 (10%) held the same baseline, and 17 (59%) increased their usage. Forty-eight percent of patients subjectively felt like cannabis helped them mitigate their opioid intake but this sentiment did not predict who actually stopped opioid usage. There were no variables that predicted who stopped opioids, except that those who used higher doses of cannabis were more likely to stop, which suggests that some patients might be able to stop opioids by using cannabis, particularly those who are dosed at higher levels.
Conclusions: In this long-term observational study, cannabis use worked as an alternative to prescription opioids in just over half of patients with low back pain and as an adjunct to diminish use in some chronic opioid users.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32923663/
“Cannabis has been used for centuries as an analgesic and has been shown to reduce chronic pain. In this long-term observational study of a single-center cannabis medical practice site, the addition of cannabis use worked as an alternative to prescription opioids in 50% of patients with chronic back pain. It worked as an adjunct to diminish use in some chronic opioid users. There was only one variable that predicted those who were able to stop opioids suggesting that some patients might be able to stop opioids by using cannabis and that those who do not stop opioids may not be titrated at doses of cannabis high enough to achieve the desired effect necessary to diminish or stop their opioid usage.”

 “Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain.
“Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain. “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.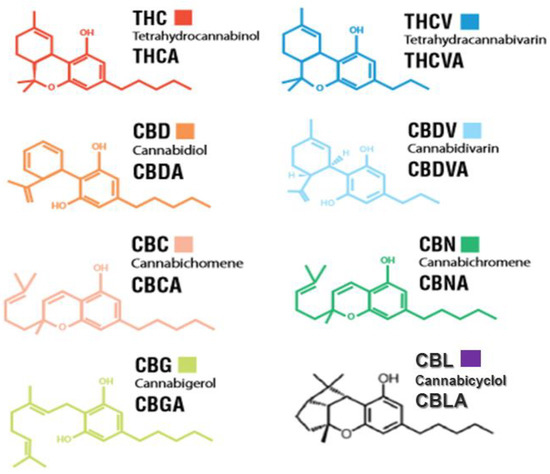
 “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
 “The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of oral transmucosal (OTM) cannabidiol (CBD), in addition to a multimodal pharmacological treatment for chronic osteoarthritis-related pain in dogs.
“The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of oral transmucosal (OTM) cannabidiol (CBD), in addition to a multimodal pharmacological treatment for chronic osteoarthritis-related pain in dogs. “Objectives
“Objectives “Globally, chronic pain is a major therapeutic challenge and affects more than 15% of the population. As patients with painful terminal diseases may face unbearable pain, there is a need for more potent analgesics.
“Globally, chronic pain is a major therapeutic challenge and affects more than 15% of the population. As patients with painful terminal diseases may face unbearable pain, there is a need for more potent analgesics. “Diabetes is a chronic disease associated with a high number of complications such as peripheral neuropathy, which causes sensorial disturbances and may lead to the development of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). The current treatment for DNP is just palliative and the drugs may cause severe adverse effects, leading to discontinuation of treatment. Thus, new therapeutic targets need to be urgently investigated.
“Diabetes is a chronic disease associated with a high number of complications such as peripheral neuropathy, which causes sensorial disturbances and may lead to the development of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). The current treatment for DNP is just palliative and the drugs may cause severe adverse effects, leading to discontinuation of treatment. Thus, new therapeutic targets need to be urgently investigated. “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible chronic neurodegenerative disorder that occurs when neurons in the brain degenerate and die. Pain frequently arises in older patients with neurodegenerative diseases including AD. However, the presence of pain in older people is usually overlooked with cognitive dysfunctions. Most of the times dementia patients experience moderate to severe pain but the development of severe cognitive dysfunctions tremendously affects their capability to express the presence of pain. Currently, there are no effective treatments against AD that emphasize the necessity for increasing research to develop novel drugs for treating or preventing the disease process. Furthermore, the prospective therapeutic use of cannabinoids in AD has been studied for the past few years. In this regard, targeting the endocannabinoid system has considered as a probable therapeutic strategy to control several associated pathological pathways, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation for the management of AD. In this review, we focus on recent studies about the role of cannabinoids for the treatment of pain and related neuropathological changes in AD.”
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible chronic neurodegenerative disorder that occurs when neurons in the brain degenerate and die. Pain frequently arises in older patients with neurodegenerative diseases including AD. However, the presence of pain in older people is usually overlooked with cognitive dysfunctions. Most of the times dementia patients experience moderate to severe pain but the development of severe cognitive dysfunctions tremendously affects their capability to express the presence of pain. Currently, there are no effective treatments against AD that emphasize the necessity for increasing research to develop novel drugs for treating or preventing the disease process. Furthermore, the prospective therapeutic use of cannabinoids in AD has been studied for the past few years. In this regard, targeting the endocannabinoid system has considered as a probable therapeutic strategy to control several associated pathological pathways, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation for the management of AD. In this review, we focus on recent studies about the role of cannabinoids for the treatment of pain and related neuropathological changes in AD.”