 “Cannabis sativa L. turned out to be a valuable source of chemical compounds of various structures, showing pharmacological activity. The most important groups of compounds include phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
“Cannabis sativa L. turned out to be a valuable source of chemical compounds of various structures, showing pharmacological activity. The most important groups of compounds include phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
The pharmacological activity of Cannabis (in epilepsy, sclerosis multiplex (SM), vomiting and nausea, pain, appetite loss, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), Parkinson’s disease, Tourette’s syndrome, schizophrenia, glaucoma, and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)), which has been proven so far, results from the affinity of these compounds predominantly for the receptors of the endocannabinoid system (the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), type two (CB2), and the G protein-coupled receptor 55 (GPR55)) but, also, for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), glycine receptors, serotonin receptors (5-HT), transient receptor potential channels (TRP), and GPR, opioid receptors.
The synergism of action of phytochemicals present in Cannabis sp. raw material is also expressed in their increased bioavailability and penetration through the blood-brain barrier. This review provides an overview of phytochemistry and pharmacology of compounds present in Cannabis extracts in the context of the current knowledge about their synergistic actions and the implications of clinical use in the treatment of selected diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/2/778
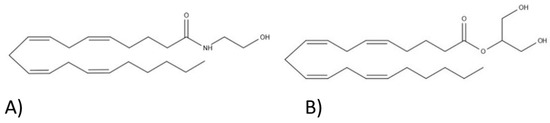

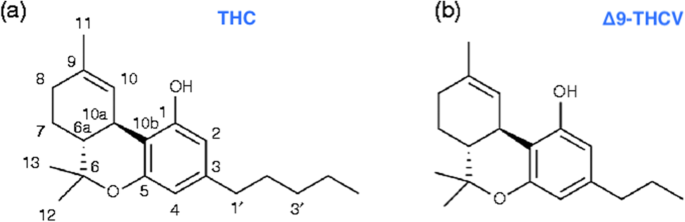 “Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabis-derived compound with unique properties that set it apart from the more common cannabinoids, such as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The main advantage of THCV over THC is the lack of psychoactive effects.
“Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabis-derived compound with unique properties that set it apart from the more common cannabinoids, such as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The main advantage of THCV over THC is the lack of psychoactive effects.  “Background and purpose:
“Background and purpose:  “Introduction:
“Introduction:  “Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from  “Background:
“Background:  “Nowadays cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the major causes for the reduction of the quality of life.
“Nowadays cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the major causes for the reduction of the quality of life.
 “Introduction:
“Introduction: “Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.
“Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.