 “Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
Results: The mean monthly dosage of cannabis consumed was 42.4 grams; 95.8% of respondents reported not consuming cannabis regularly before being diagnosed with cancer; the most common way of administration was smoking, and most of the participants reported taking cannabis throughout the day. The most common symptoms for which participants took medical cannabis were pain (n = 169, 88.9%), sleeping disorder (n = 144, 75.8%) and anxiety (n = 79, 41.6%). Twenty patients (10.5%) reported on mild side (or adverse) effects.
Conclusions: This study indicates that cancer survivors may indeed consume cannabis for symptom relief, and not merely for recreational purposes. Although our findings point to perceived safety and efficacy of medical cannabis for cancer survivors, more research is needed to study the adequate role that cannabis may have for treating symptoms associated with cancer survivorship.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33197667/
“In conclusion, despite the many challenges and uncertainties, cannabis is being slowly diffused into healthcare. Survivors who have ongoing symptoms as a result of their prior treatments should be carefully assessed as to whether there is a medical need for which cannabis may be helpful. Indeed, patients and physicians should establish and maintain a therapeutic alliance in which medical needs and potential treatments, including medical cannabis, are honestly discussed and mutually considered and agreed upon.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0965229920318598?via%3Dihub

 “The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a deadly disease afflicting millions. The pandemic continues affecting population due to nonavailability of drugs and vaccines. The pathogenesis and complications of infection mainly involve hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Thus, therapeutic strategies rely on repurposing of drugs aimed at reducing infectivity and inflammation and modulate immunity favourably.
“The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a deadly disease afflicting millions. The pandemic continues affecting population due to nonavailability of drugs and vaccines. The pathogenesis and complications of infection mainly involve hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Thus, therapeutic strategies rely on repurposing of drugs aimed at reducing infectivity and inflammation and modulate immunity favourably.
 “The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease.
“The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease. “The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.
“The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.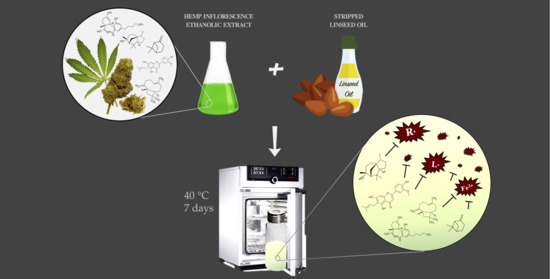
 “Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation.
“Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation. “Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
“Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids. “This article retraces the story of cannabis from the earliest contacts of humans with the plant to its subsequent global expansion, its medicinal uses, and the discovery of the endocannabinoid system in the 20th century. Cannabis was attested to around 12 000 years ago near the Altai Mountains in Central Asia, and since then, cannabis seeds have accompanied the migration of nomadic peoples. Records of the medicinal use of cannabis appear before the Common Era in China, Egypt, and Greece (Herodotus), and later in the Roman empire (Pliny the Elder, Dioscorides, Galen). In the 19th century, orientalists like Silvestre de Sacy, and Western physicians coming into contact with Muslim and Indian cultures, like O’Shaughnessy and Moreau de Tours, introduced the medicinal use of cannabis into Europe. The structure of the main psychoactive phytocannabinoid, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), was determined in Israel by Mechoulam and Gaoni in 1964. This discovery opened the gate for many of the subsequent developments in the field of endocannabinoid system (ECS) research. The advances in the scientific knowledge of the ECS place the debate on cannabis liberalization in a new context.”
“This article retraces the story of cannabis from the earliest contacts of humans with the plant to its subsequent global expansion, its medicinal uses, and the discovery of the endocannabinoid system in the 20th century. Cannabis was attested to around 12 000 years ago near the Altai Mountains in Central Asia, and since then, cannabis seeds have accompanied the migration of nomadic peoples. Records of the medicinal use of cannabis appear before the Common Era in China, Egypt, and Greece (Herodotus), and later in the Roman empire (Pliny the Elder, Dioscorides, Galen). In the 19th century, orientalists like Silvestre de Sacy, and Western physicians coming into contact with Muslim and Indian cultures, like O’Shaughnessy and Moreau de Tours, introduced the medicinal use of cannabis into Europe. The structure of the main psychoactive phytocannabinoid, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), was determined in Israel by Mechoulam and Gaoni in 1964. This discovery opened the gate for many of the subsequent developments in the field of endocannabinoid system (ECS) research. The advances in the scientific knowledge of the ECS place the debate on cannabis liberalization in a new context.” “Introduction and objectives: Previous studies reveal conflicting data on the effect of cannabis use in patients with cirrhosis. This research evaluates the impact of cannabis on hepatic decompensation, health care utilization, and mortality in patients with cirrhosis.
“Introduction and objectives: Previous studies reveal conflicting data on the effect of cannabis use in patients with cirrhosis. This research evaluates the impact of cannabis on hepatic decompensation, health care utilization, and mortality in patients with cirrhosis. “Objective: To evaluate the use of a Cannabis sativa oil in the management of patients diagnosed with primary burning mouth syndrome (BMS).
“Objective: To evaluate the use of a Cannabis sativa oil in the management of patients diagnosed with primary burning mouth syndrome (BMS). “The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
“The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.