 “Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are Cannabis sativa terpenophenols.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are Cannabis sativa terpenophenols.
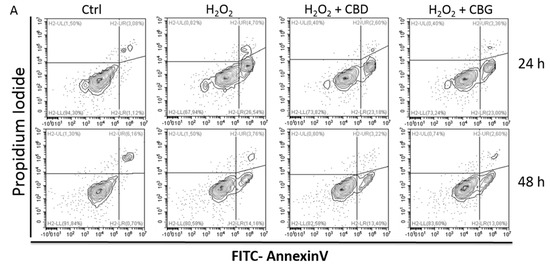
Although CBD’s effectiveness against neurological diseases has already been demonstrated, nothing is known about CBG. Therefore, a comparison of the effects of these compounds was performed in two experimental models mimicking the oxidative stress and neurotoxicity occurring in neurological diseases.
Rat astrocytes were exposed to hydrogen peroxide and cell viability, reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis occurrence were investigated. Cortexes were exposed to K+ 60 mM depolarizing stimulus and serotonin (5-HT) turnover, 3-hydroxykinurenine and kynurenic acid levels were measured. A proteomic analysis and bioinformatics and docking studies were performed.
Both compounds exerted antioxidant effects in astrocytes and restored the cortex level of 5-HT depleted by neurotoxic stimuli, whereas sole CBD restored the basal levels of 3-hydroxykinurenine and kynurenic acid. CBG was less effective than CBD in restoring the levels of proteins involved in neurotransmitter exocytosis. Docking analyses predicted the inhibitory effects of these compounds towards the neurokinin B receptor.
Conclusion: The results in the in vitro system suggest brain non-neuronal cells as a target in the treatment of oxidative conditions, whereas findings in the ex vivo system and docking analyses imply the potential roles of CBD and CBG as neuroprotective agents.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32443623/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/10/3575

 “Cannabis sativa or Indian hemp (subfamily Cannaboideae of family Moraceae) is an annual herbaceous plant, native to central and western Asia, cultivated for medicinal properties and for hemp, which is a natural textile fiber. The plant contains over 400 chemical compounds, of which approximately 80 biologically active chemical molecules. The most important cannabis compounds are cannabinoids formed by a terpene combined with resorcinol, or, according to a different nomenclature, by a benzopyranic ring system. There are about sixty cannabinoids, of which the most important psychoactive compound is tetrahydrocannabinol (TCH), in particular the isomer delta (Δ9-THC). Other identified compounds are
“Cannabis sativa or Indian hemp (subfamily Cannaboideae of family Moraceae) is an annual herbaceous plant, native to central and western Asia, cultivated for medicinal properties and for hemp, which is a natural textile fiber. The plant contains over 400 chemical compounds, of which approximately 80 biologically active chemical molecules. The most important cannabis compounds are cannabinoids formed by a terpene combined with resorcinol, or, according to a different nomenclature, by a benzopyranic ring system. There are about sixty cannabinoids, of which the most important psychoactive compound is tetrahydrocannabinol (TCH), in particular the isomer delta (Δ9-THC). Other identified compounds are  “The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.
“The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.

 “In traditional medicine, Cannabis sativa has been prescribed for a variety of diseases. Today, the plant is largely known for its recreational purpose, but it may find a way back to what it was originally known for: a herbal remedy. Most of the plant’s ingredients, such as Δ-tetrahydrocannabinol,
“In traditional medicine, Cannabis sativa has been prescribed for a variety of diseases. Today, the plant is largely known for its recreational purpose, but it may find a way back to what it was originally known for: a herbal remedy. Most of the plant’s ingredients, such as Δ-tetrahydrocannabinol,  “Neuroinflammation is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this study, we investigate the anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties of two non-psychoactive phytocannabinoids, cannabigerol (CBG) and
“Neuroinflammation is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this study, we investigate the anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties of two non-psychoactive phytocannabinoids, cannabigerol (CBG) and  “Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment.
“Ovarian cancer, with over a 90% reoccurrence within 18 months of treatment, and approximately a 30% mortality rate after 5 years, is the leading cause of death in cases of gynaecological malignancies. Acquired resistance, and toxic side effects by clinically used agents are major challenges associated with current treatments, indicating the need for new approaches in ovarian cancer treatment. “In a recent study, we described the neuroprotective properties of VCE-003.2-an aminoquinone derivative of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabigerol (CBG)-administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) in an inflammatory model of Parkinson’s disease (PD). We also demonstrated that these properties derive from its activity on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ, in particular at a regulatory site within this receptor type.
“In a recent study, we described the neuroprotective properties of VCE-003.2-an aminoquinone derivative of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabigerol (CBG)-administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) in an inflammatory model of Parkinson’s disease (PD). We also demonstrated that these properties derive from its activity on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ, in particular at a regulatory site within this receptor type.

