 “Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system.
“Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system.
Purpose: The objective of the present paper is to elucidate the role of Cannabis consumption in GI system. An additional aim is to review the information on the function of Cannabis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods and results: This review summarizes the recent findings on the role of cannabinoid receptors, their synthetic or natural ligands, as well as their metabolizing enzymes in normal GI function and its disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and possible adverse events. The synergism or antagonism between Cannabis’ active ingredients and the “entourage” plays a role in the efficacy of various strains. Some elements of Cannabis may alter disease severity as over-activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 can lead to changes of the commensal gut flora. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) contributes to gut homeostasis. The ability of ECS to modulate inflammatory responses demonstrates the capacity of ECS to preserve gastrointestinal (GI) function. Alterations of the ECS may predispose patients to pathologic disorders, including IBD. Clinical studies in IBD demonstrate that subjects benefit from Cannabis consumption as seen through a reduction of the IBD-inflammation, as well as through a decreased need for other medication. NAFLD is characterized by fat accumulation in the liver. The occurrence of inflammation in NAFLD leads to non-alcoholic-steatohepatitis (NASH). The use of Cannabis might reduce liver inflammation.
Conclusions: With limited evidence of efficacy and safety of Cannabis in IBD, IBS, and NAFLD, randomized controlled studies are required to examine its therapeutic efficacy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32762830/
https://journals.library.ualberta.ca/jpps/index.php/JPPS/article/view/31242

 “Although several lines of evidence support the hypothesis of a dysregulation of serotoninergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), there is also evidence for an involvement of other pathways such as the GABAergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic systems.
“Although several lines of evidence support the hypothesis of a dysregulation of serotoninergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), there is also evidence for an involvement of other pathways such as the GABAergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic systems. “The etiopathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) remains largely unclear.
“The etiopathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) remains largely unclear.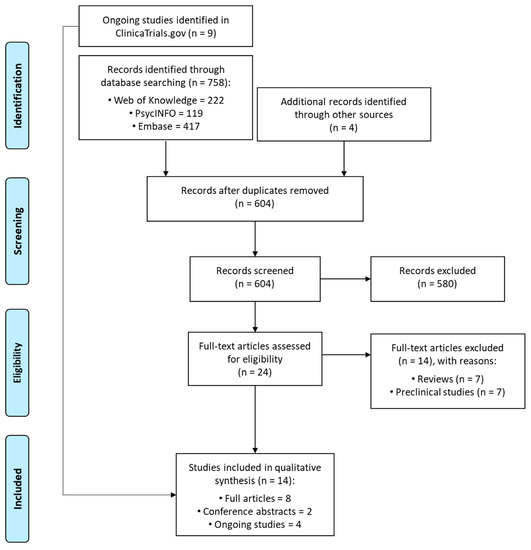
 “Alcohol is a psychoactive substance highly used worldwide, whose harmful use might cause a broad range of mental and behavioural disorders. Underlying brain impact, the neuroinflammatory response induced by alcohol is recognised as a key contributing factor in the progression of other neuropathological processes, such as neurodegeneration. These sequels are determined by multiple factors, including age of exposure.
“Alcohol is a psychoactive substance highly used worldwide, whose harmful use might cause a broad range of mental and behavioural disorders. Underlying brain impact, the neuroinflammatory response induced by alcohol is recognised as a key contributing factor in the progression of other neuropathological processes, such as neurodegeneration. These sequels are determined by multiple factors, including age of exposure.
 “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.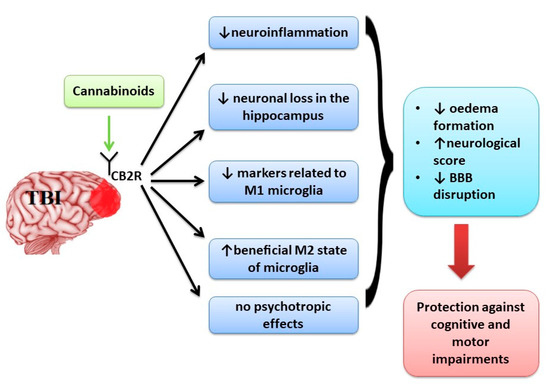
 “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”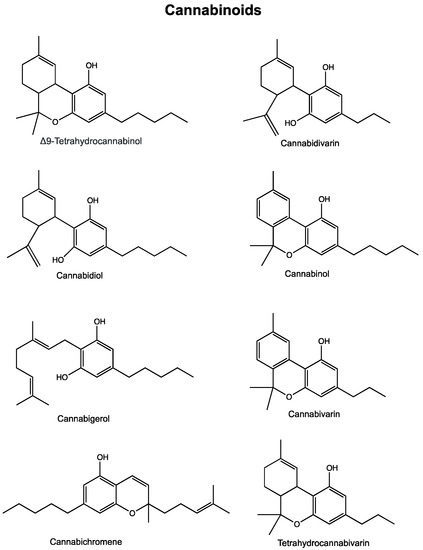
 “Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury. “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. “During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions.
“During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions. “Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
“Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”