https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32648908/
“Therapeutic intervention in the dysregulation of the ECS will no doubt involve new phytocannabinoids and various synthetic CBs with which to control an increasing list of ECS- related pathologies.”



https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32648908/
“Therapeutic intervention in the dysregulation of the ECS will no doubt involve new phytocannabinoids and various synthetic CBs with which to control an increasing list of ECS- related pathologies.”

“Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance-P and dural mast cells are main contributors in neurogenic inflammation underlying migraine pathophysiology.
Modulation of endocannabinoid system attenuates migraine pain, but its mechanisms of action remains unclear.
We investigated receptor mechanisms mediating anti-neuroinflammatory effects of endocannabinoid system modulation in in-vivo migraine model and ex-vivo hemiskull preparations in rats.
Selective ligands targeting CB1 and CB2 receptors may provide novel and effective treatment strategies against migraine.”
 “Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.”
“Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.”
 “Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property.
“Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property.
The distribution of cannabinoid receptors type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) in blood vessels and tumor tissue of astrocytoma is still controversial. Asrocytoma tissues were collected from 45 patients under the condition of tumor-related neurosurgical operation. The expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors was assessed using immunofluorescence, quantitative real-time RT-PCR and western blotting.
The results indicated an increased expression of CB1 receptors in tumor tissue. There was a significant difference in the mount of CB2 receptors in blood vessels. More was observed in the grade III and glioblastoma (grade IV) than astrocytoma of grade II and control.
This study suggested that, the expression increase of cannabinoid receptors is an index for astrocytoma malignancy and can be targeted as a therapeutic approach for the inhibition of astrocytoma growth among patients.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32623617/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11033-020-05636-8
 “Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia.
“Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia.
A review in 2017 summarized positive findings for therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids in agitation of AD and dementia, but there was no definitive conclusion because of varying cannabinoid products. Cannabinoids were shown to be well tolerated, with few short-term side effects. This differs from first-line medications utilized for dementia behaviors, which can have unwanted side effects. Further research regarding the safety, efficacy, and variability of these products in older people is needed.”
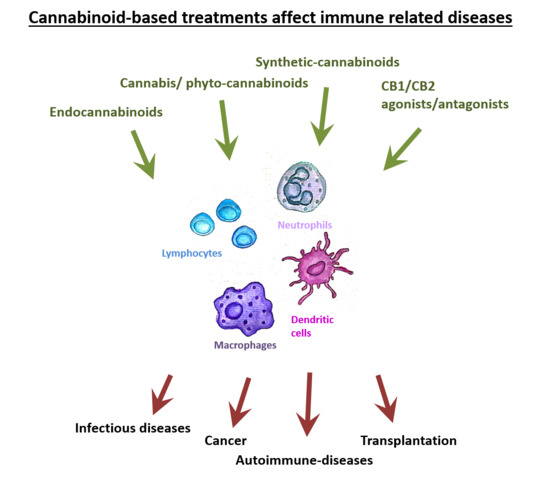
 “The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
“The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
While Cannabis is not yet registered as a drug, the potential of cannabinoid-based medicines for the treatment of various conditions has led many countries to authorize their clinical use. However, the data from basic and medical research dedicated to medical Cannabis is currently limited.
A variety of pathological conditions involve dysregulation of the immune system. For example, in cancer, immune surveillance and cancer immuno-editing result in immune tolerance. On the other hand, in autoimmune diseases increased immune activity causes tissue damage.
Immuno-modulating therapies can regulate the immune system and therefore the immune-regulatory properties of cannabinoids, suggest their use in the therapy of immune related disorders.
In this contemporary review, we discuss the roles of the endocannabinoid system in immunity and explore the emerging data about the effects of cannabinoids on the immune response in different pathologies. In addition, we discuss the complexities of using cannabinoid-based treatments in each of these conditions.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32585801/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/12/4448
“Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are known to produce antinociceptive effects mainly through peripheral COX-inhibition. Paracetamol and dipyrone are different from classical NSAIDs, because they exert weak anti-inflammatory activity; mechanisms other than peripheral COX inhibition appear to play role in their antinociceptive actions. In this review, we specified classical NSAIDs, paracetamol and dipyrone as “non-opioid analgesics” and discussed the mechanisms mediating participation of the endocannabinoid system in the antinociceptive effects of these analgesics. Non-opioid analgesics and their metabolites may activate cannabinoid receptors. In addition, several mechanisms are implicated in the elevation of endocannabinoid levels following administration of non-opioid analgesics. Of these, reduction of endocannabinoid degradation via FAAH and/or COX-2 inhibition, accumulation of arachidonic acid to endocannabinoid biosynthesis following COX inhibition, inhibition of cellular uptake of endocannabinoids directly or following inhibition of nitric oxide synthase production, and induction of endocannabinoid release are among the proposed mechanisms.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32551466/
http://balkanmedicaljournal.org/uploads/pdf/pdf_BMJ_2226.pdf
 “Cannabis-inspired medical products are garnering increasing attention from the scientific community, general public, and health policy makers. A plethora of scientific literature demonstrates intricate engagement of the endocannabinoid system with human immunology, psychology, developmental processes, neuronal plasticity, signal transduction, and metabolic regulation. Despite the therapeutic potential, the adverse psychoactive effects and historical stigma, cannabinoids have limited widespread clinical application. Therefore, it is plausible to weigh carefully the beneficial effects of cannabinoids against the potential adverse impacts for every individual. This is where the concept of “personalized medicine” as a promising approach for disease prediction and prevention may take into the account. The goal of this review is to provide an outline of the endocannabinoid system, including endocannabinoid metabolizing pathways, and will progress to a more in-depth discussion of the therapeutic interventions by endocannabinoids in various neurological disorders.”
“Cannabis-inspired medical products are garnering increasing attention from the scientific community, general public, and health policy makers. A plethora of scientific literature demonstrates intricate engagement of the endocannabinoid system with human immunology, psychology, developmental processes, neuronal plasticity, signal transduction, and metabolic regulation. Despite the therapeutic potential, the adverse psychoactive effects and historical stigma, cannabinoids have limited widespread clinical application. Therefore, it is plausible to weigh carefully the beneficial effects of cannabinoids against the potential adverse impacts for every individual. This is where the concept of “personalized medicine” as a promising approach for disease prediction and prevention may take into the account. The goal of this review is to provide an outline of the endocannabinoid system, including endocannabinoid metabolizing pathways, and will progress to a more in-depth discussion of the therapeutic interventions by endocannabinoids in various neurological disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32549916/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs13167-020-00203-4
 “The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.
“The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.
This work aims to investigate if the anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are mediated by PI3Kγ.
CDB increased latency and reduced the severity of pilocarpine-induced behavioral seizures, as well as prevented postictal changes, such as neurodegeneration, microgliosis and astrocytosis, in WT animals, but not in PI3Kγ-/-. CBD in vivo effects were abolished by pharmacological inhibition of cannabinoid receptor or mTOR. In vitro, PI3Kγ inhibition or deficiency also changed CBD protection observed in glutamate-induced cell death assay. Thus, we suggest that the modulation of PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway is involved in the anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of CBD.
These findings are important not only for the elucidation of the mechanisms of action of CBD, which are currently poorly understood, but also to allow the prediction of therapeutic and side effects, ensuring efficacy and safety in the treatment of patients with epilepsy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32574650/
“CBD is anticonvulsant in a model of pilocarpine-induced behavioral seizures. CB1 receptor mediates the effects of CBD. PI3Kγ pathway mediates the anticonvulsant neuroprotective effects of CBD.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0028390820302240?via%3Dihub
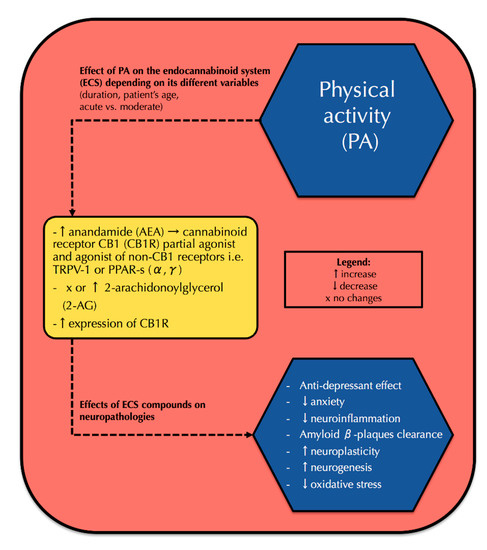
 “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
Numerous data indicate a distinct correlation between the altered endocannabinoid signaling and different aspects of brain physiology, such as memory or neurogenesis. Moreover, the endocannabinoid system is widely regarded as a crucial factor in the development of neuropathologies. Thus, targeting those disorders via synthetic cannabinoids, as well as phytocannabinoids, becomes a widespread research issue.
Over the last decade, the endocannabinoid system has been extensively studied for its correlation with physical activity. Recent data showed that physical activity correlates with elevated endocannabinoid serum concentrations and increased cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1R) expression in the brain, which results in positive neurological effects including antidepressant effect, ameliorated memory, neuroplasticity development, and reduced neuroinflammation. However, none of the prior reviews presented a comprehensive correlation between physical activity, the endocannabinoid system, and neuropathologies.
Thus, our review provides a current state of knowledge of the endocannabinoid system, its action in physical activity, as well as neuropathologies and a possible correlation between all those fields. We believe that this might contribute to finding a new preventive and therapeutic approach to both neurological and neurodegenerative disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32545780/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/12/4221