 “Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.
“Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.
Due to the similarities between industrial hemp (fiber and grain) and the narcotic/medical type of Cannabis, the production of industrial hemp was prohibited in most countries, wiping out centuries of learning and genetic resources. In the past two decades, most countries have legalized industrial hemp production, prompting a significant amount of research on the health benefits of hemp and hemp products.
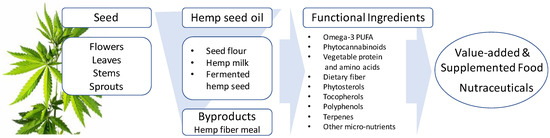
Current research is yet to verify the various health claims of the numerous commercially available hemp products. Hence, this review aims to compile recent advances in the science of industrial hemp, with respect to its use as value-added functional food ingredients/nutraceuticals and health benefits, while also highlighting gaps in our current knowledge and avenues of future research on this high-value multi-use plant for the global food chain.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32906622/
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/18/4078

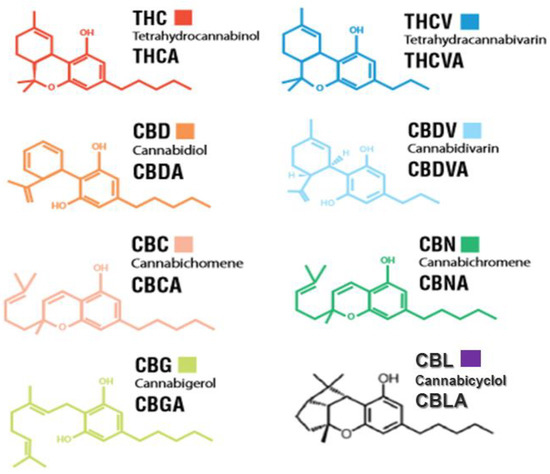
 “The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator.
“The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator. “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
 “Previous preclinical studies have demonstrated that cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG), two non-psychotomimetic phytocannabinoids from Cannabis sativa, induce neuroprotective effects on toxic and neurodegenerative processes.
“Previous preclinical studies have demonstrated that cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG), two non-psychotomimetic phytocannabinoids from Cannabis sativa, induce neuroprotective effects on toxic and neurodegenerative processes. “Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) is a potent activator of Vβ8+T-cells resulting in the clonal expansion of ∼30% of the T-cell pool. Consequently, this leads to the release of inflammatory cytokines, toxic shock, and eventually death.
“Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) is a potent activator of Vβ8+T-cells resulting in the clonal expansion of ∼30% of the T-cell pool. Consequently, this leads to the release of inflammatory cytokines, toxic shock, and eventually death. “Staphylococcal enterotoxin‐B (SEB) is one of the most potent bacterial superantigens that exerts profound toxic effects by inducing cytokine storm. When SEB is inhaled, it can cause Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which is often fatal and currently there are no effective treatment modalities.
“Staphylococcal enterotoxin‐B (SEB) is one of the most potent bacterial superantigens that exerts profound toxic effects by inducing cytokine storm. When SEB is inhaled, it can cause Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which is often fatal and currently there are no effective treatment modalities. “Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) causes up to 40% mortality in humans and is difficult to treat. ARDS is also one of the major triggers of mortality associated with coronavirus-induced disease (COVID-19). We used a mouse model of ARDS induced by Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), which triggers 100% mortality, to investigate the mechanisms through which Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) attenuates ARDS.
“Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) causes up to 40% mortality in humans and is difficult to treat. ARDS is also one of the major triggers of mortality associated with coronavirus-induced disease (COVID-19). We used a mouse model of ARDS induced by Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), which triggers 100% mortality, to investigate the mechanisms through which Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) attenuates ARDS. “Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is evolving across the world and new treatments are urgently needed as with vaccines to prevent the illness and stem the contagion. The virus affects not only the lungs but also other tissues, thus lending support to the idea that COVID-19 is a systemic disease. The current vaccine and treatment development strategies ought to consider such systems medicine perspectives rather than a narrower focus on the lung infection only.
“Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is evolving across the world and new treatments are urgently needed as with vaccines to prevent the illness and stem the contagion. The virus affects not only the lungs but also other tissues, thus lending support to the idea that COVID-19 is a systemic disease. The current vaccine and treatment development strategies ought to consider such systems medicine perspectives rather than a narrower focus on the lung infection only. “Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations.
“Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations.