 “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32708138/
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/7/1985
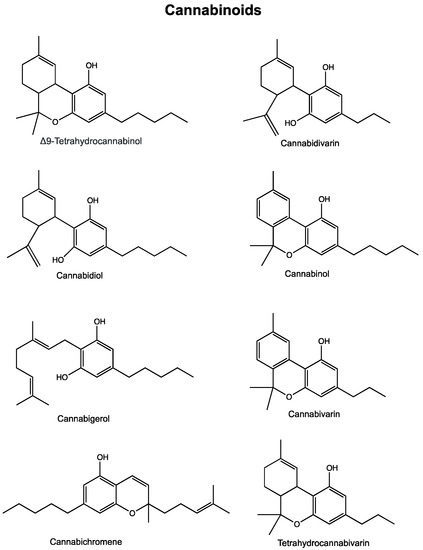

 “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.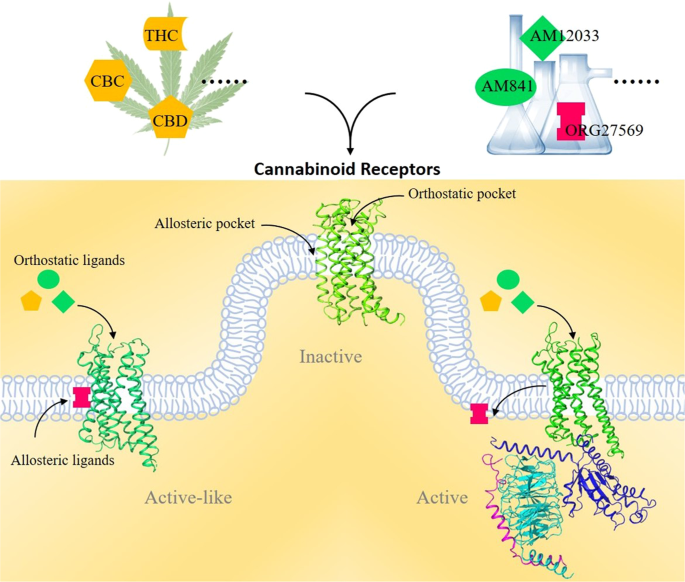
 “HIV is associated with disruptions in cognition and brain function.
“HIV is associated with disruptions in cognition and brain function. “In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.”
“In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.” “We observed that cannabidiol supplements were highly effective in treating an infant boy with drug-resistant early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, eliminating his intractable tonic seizures.
“We observed that cannabidiol supplements were highly effective in treating an infant boy with drug-resistant early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, eliminating his intractable tonic seizures. “Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis.
“Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis. “Self-reported cannabis use has increased since its recent legalization in many states.
“Self-reported cannabis use has increased since its recent legalization in many states. “In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
“In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
 “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. “During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions.
“During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions.